Linux Chmod Table
Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog Mvps Net Tutorials

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

14 Permission And Modification Times

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Chmod 555
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options.

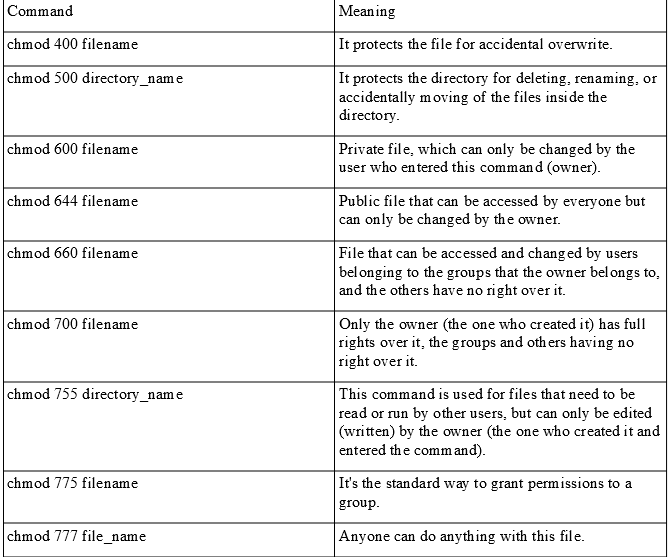
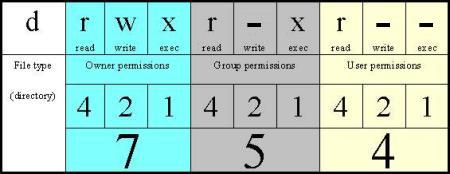
Linux chmod table. There are three sets of permissions. It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers. If you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks:.
Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmod command to change file permissions on a file or directory. And = causes them to be. Chmod command has the following syntax:.
Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. You can read chmod u+r as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permission.
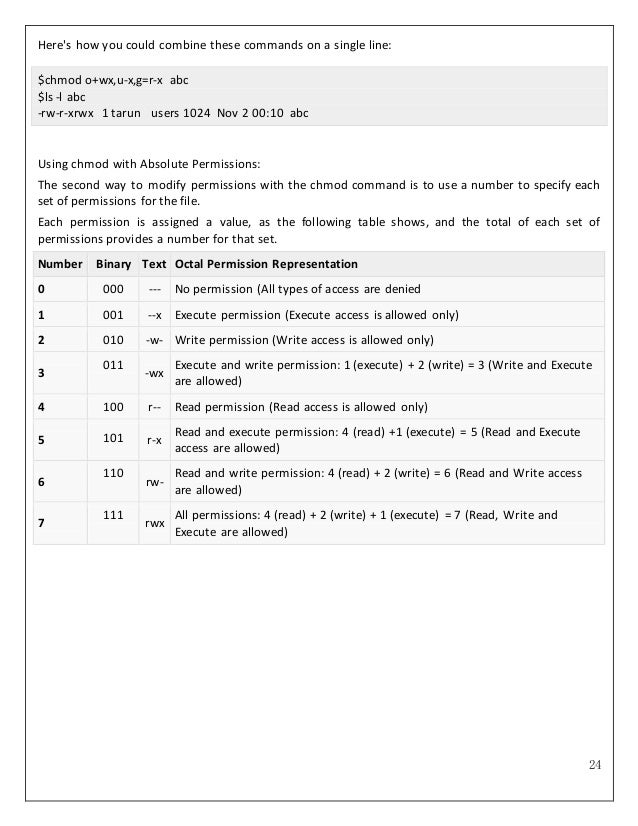
Absolute Mode - Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions). Chmod all directories to 711;. Chmod option mode files Options.
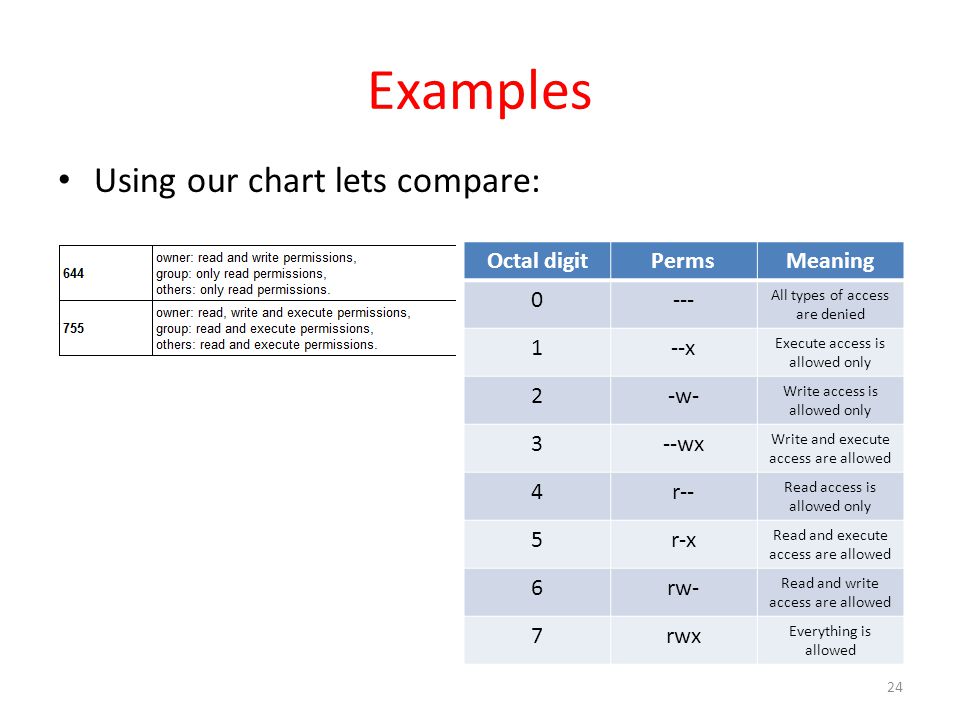
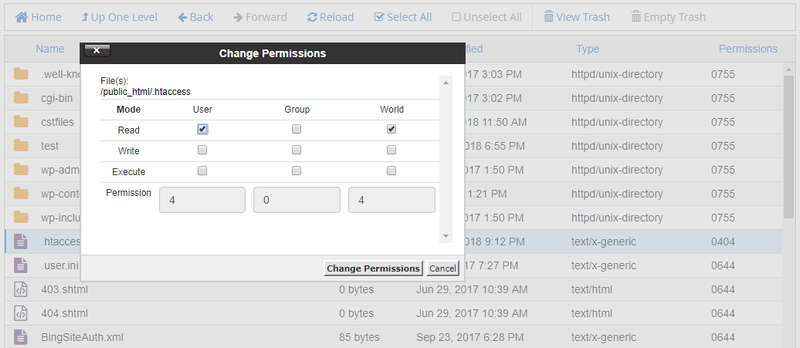
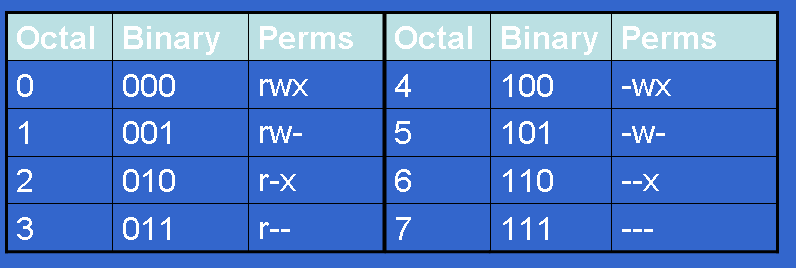
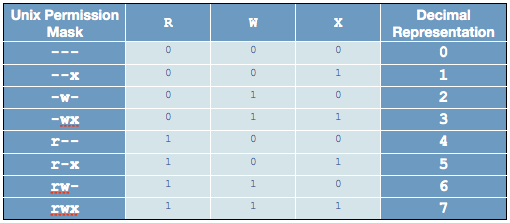
If three numerals are given, you're setting the read, write and execute bits for the file's owner, group and others (everyone else). The permissions passed as an argument to chmod are specified as an octal value. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g.
The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file. They are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissions. Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions.
Chmod command in Linux. Linux is a clone of UNIX, the multi-user operating system which can be accessed by many users simultaneously.Linux can also be used in mainframes and servers without any modifications. This is known as symbolic mode.
Make a Script Executable. The syntax for the chmod command is:. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system. I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:.
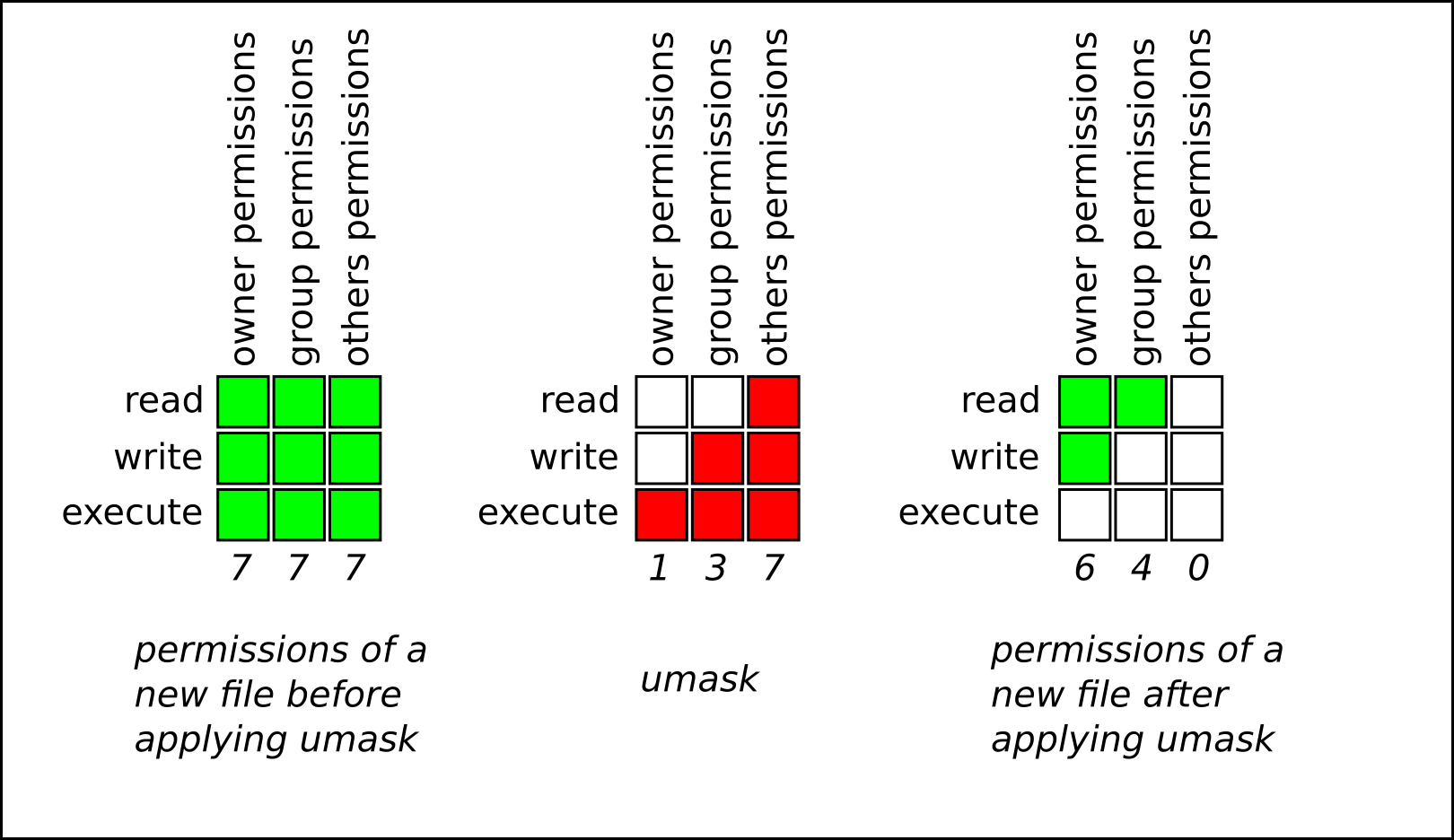
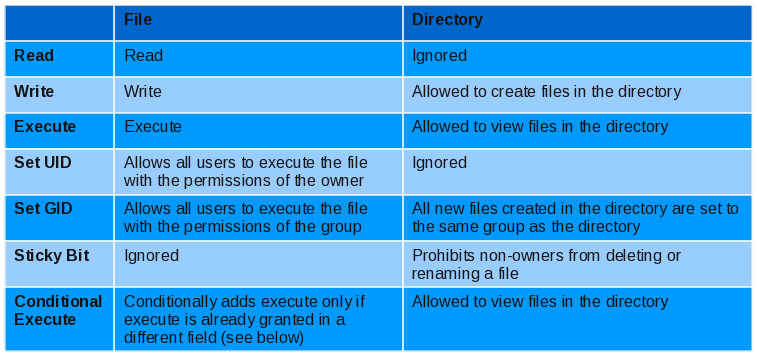
Umask or file mode creation mask is a grouping of bits, each of which restricts how its corresponding permission is set for newly created files or directories. This command is used for changing the mode of access. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
The difference is what permissions get set and which mode you use to set them. For example, to add execute permissions for the owner of a file you would run:. The owner of the file/directory can read and.
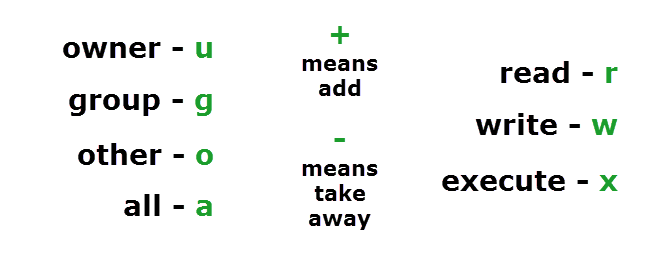
If the mask has a bit set to "1", it means the corresponding initial file permission will be disabled.A bit set to "0" in the mask means that the corresponding. Permissions on a Linux system can be managed by using three commands:. A plus (+) symbol adds a permission, and a minus (-) symbol removes a permission.
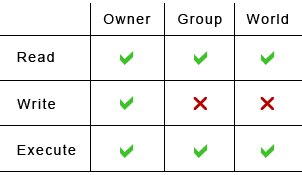
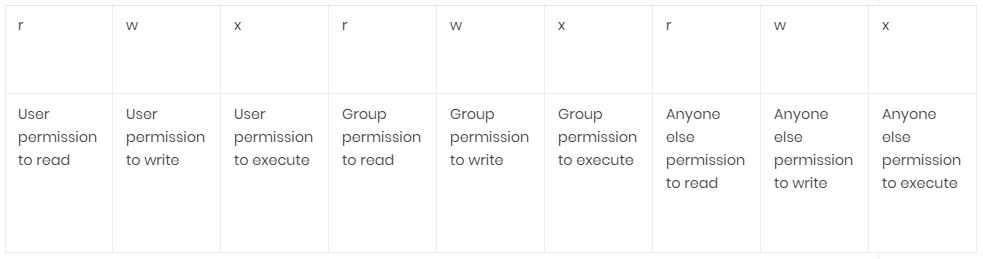
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable - = no permission. Group – The Group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users.
This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories. To quote the man chmod:. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify.
In the example -rw-r--r--, the owner permissions are rw-, indicating that the owner can read and write to the. The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux.
Chmod preserves a directory's set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits unless you explicitly specify otherwise. Linux-jwc3:/ # ls -l myfile.txt. The chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system.
Numeric format example of permission in Linux using chmod. The below table shows some examples of permission with a numeric value and text value you can set permission either numeric or text format. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats.
Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 600 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 655 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-w,o-w) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. To use chmod, you need to know about access modes.Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine exactly who can. Using chmod in Symbolic Mode.
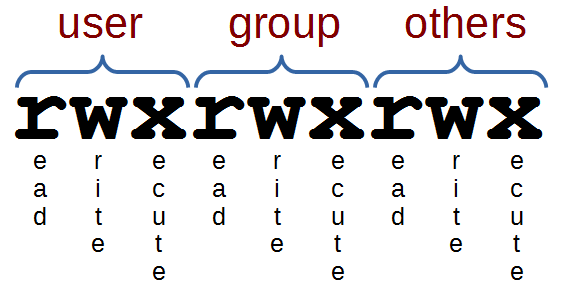
File group, and others, in that order. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.
The easiest way for a beginner to modify file or directory permissions is to use the symbolic mode. Owner – The Owner permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.;. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file.
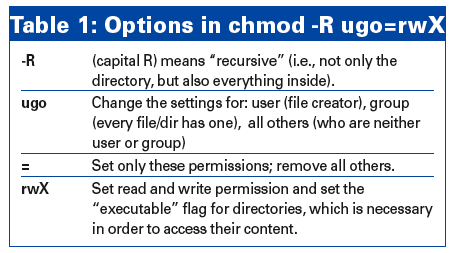
Chmod options mode filename filename1… chmod options mode directory_name. We have already described the Linux file permissions. Linux Permissions Syntax You can use this table to understand the different symbolic or octal value to use with chmod Perform chmod recursive with -R or --recursive If all your files and directories are under one parent directory then you can directly use chmod -R <dir_name> to assign the permission recursively.
By David · September 18, 12. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. The bits in the mask may be changed by invoking the umask command.
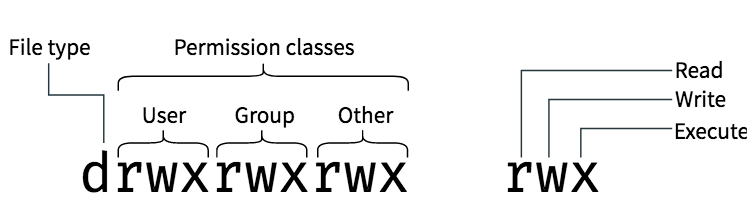
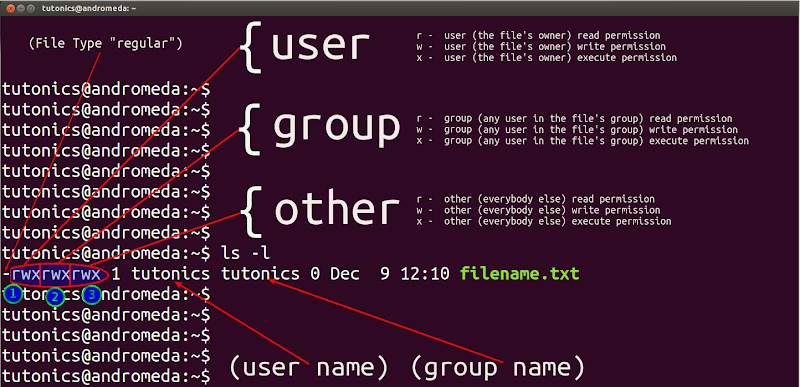
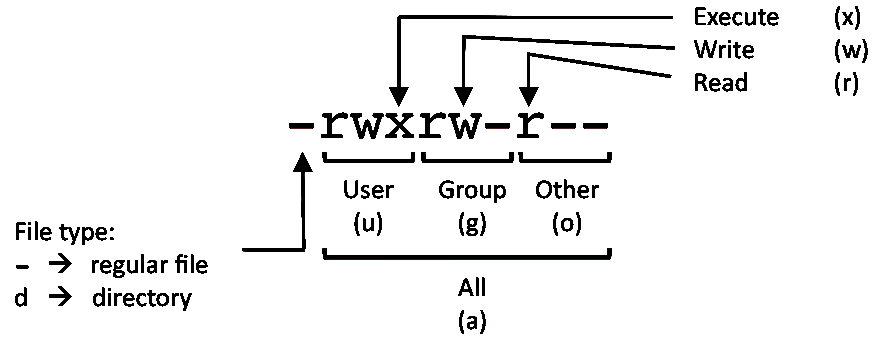
Note the multiple instances of r, w, and x.These are grouped into three sets that represent different levels of ownership:. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.
We should note that many Linux security configurations will prevent keys in the .ssh folder from being used to allow SSH access if they do not have the correct permissions applied. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros.
Each file and directory has three user based permission groups:. See Table 15–5 for the list of valid octal values. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons. Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;. Additionally server-side languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation.
The “mode” consists of three parts:. Chmod, chown and chgrp. This is why this particular command was named chmod.
But this raises security concerns as an unsolicited or malign user can corrupt, change or remove crucial data.For effective security, Linux divides authorization into 2 levels. - causes them to be removed;. It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically.
Chmod all directories that users can upload files to, to 755 (ex:. - ubuntu - red hat - debian - linux server - linux pc Home Tutorials Linux How to set chmod for a folder and all of its subfolders and files in Linux Ubuntu Terminal ?. The three user levels are Owner, Group, and Other.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. Owner or user permissions:.
This is how I remember permissions and most likely, it will help you remember it as well. Sets sticky bit, sets read, write, and execute permissions for owner, and sets read and execute permissions for group and others (this suggests that the script be retained in memory) chmod 4755 setCtrls.sh. Select the permissions you require below.
How does chmod work?. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. You can set read permission to the owner.
Chmod all files to 644;. The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply i.e. Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
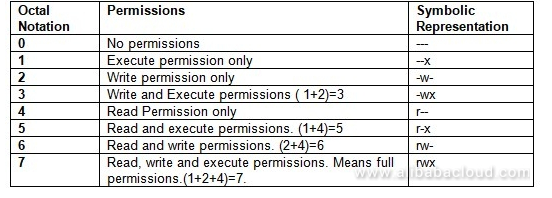
Who is specified as. Here's a summary that I have gathered. User Group Other Read 4 4 4 Write 2 2 2 Execute 1 1 1 U G O X X X Chmods:.
Chmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. How to change file permissions using chmod and chown.
Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Linux-jwc3:/ # chmod 400 myfile.txt. Now all you have to do is think of what permissions you want, add the values associated with the permissions, and type chmod followed by the total and file or directory name.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. CHMOD Permissions Reference Chart. After the directory (d) slot, the first set of three characters indicate permission settings for the owner (also known as the user).
There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings. Chmod all .htaccess files to 644 chmod all robots.txt files to 644;. Sets read, write, and execute permissions for user, and sets read permission for Group and Others:.
Who the permissions apply to, how the permissions are set and which permissions to set. Specifies the file or directory. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters.
The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files. There are two ways to use chmod — the symbolic mode and the absolute mode. Those commands respectively change the permissions of a file, change the owner of a file or change the group of a file.
The following command. Chmod all directories with directory listing (.htaccess Options +Indexes) to 755;. Chmod stands for change mode.
With chmod +x you set the executable bit for all - the owner, the owner group, and the other users. We can use chmod and chown to manipulate the file permission. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. Actually, in early Unix days, permissions were called mode of access. You can set or clear the bits with symbolic modes like u+s and g-s , and you can set (but not clear) the bits with a numeric mode.
You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions. Each numeral in the value represents three bits. 777 = rwxrwxrwx 755 = rwxr-xr-x 644 = rw-r--r-- 700 = rwx----- 750 = rwxr-x---.
Each numeral in the value represents three bits. To change the file or the directory permissions, you use the chmod (change mode) command. Linux - Solved-15 Solutions How to set chmod for a folder and all of its subfolders and files in Linux Ubuntu Terminal ?.
Chmod.(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.

Linux For Beginners Part 6 Understanding File Permission And Ownership

Linux Guide To Linux Certification Second Edition Ppt Video Online Download
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
How To Use Unix File Permissions To Increase Security Developer Drive
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux User Group And File Permission Introduction
Controlling File Permissions With Umask

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Beginner S Guide To File Permission In Linux Sharing Is Caring

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut
Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference
Linux Chmod Tips

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Ownership And Permissions
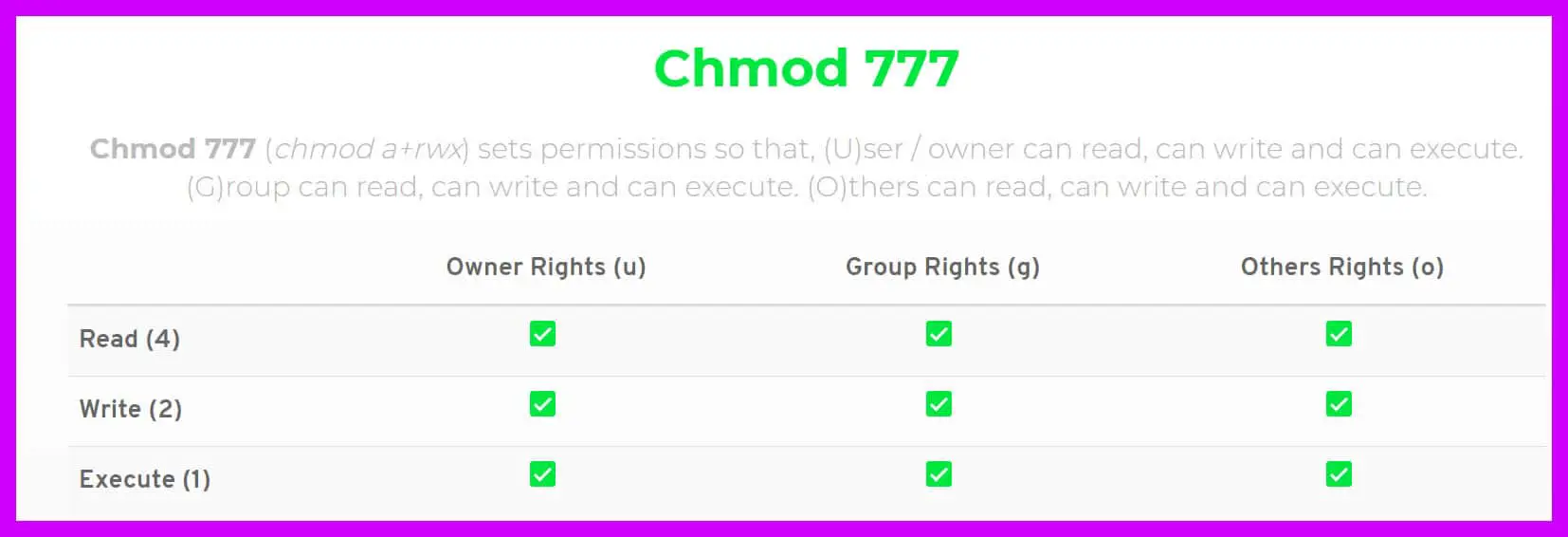
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
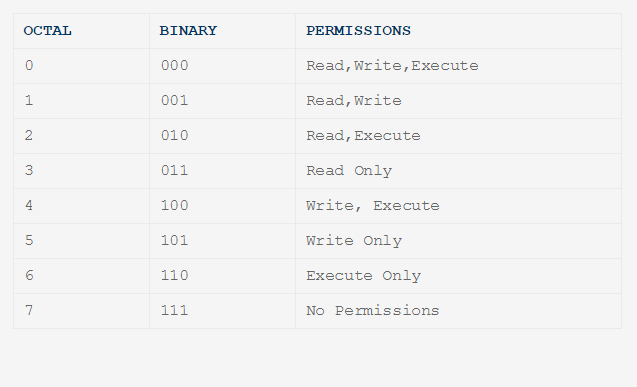
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
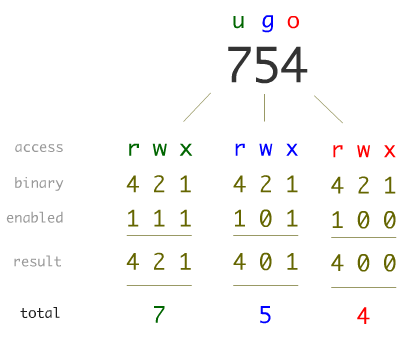
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com

Linux Users And Groups Linode

ल नक स म Chmod कम ड क य ह Computer Hindi Notes
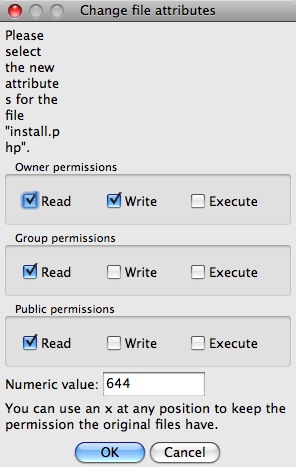
Linux Chmod How To Make A Perl Script Executable Alvinalexander Com

Chmod Change Permissions To A Specific User In Ubuntu 12 04 Ask Ubuntu

Basic Linux Commands Gooribi Inc

Introduction To Unix Family File Permissions Learning Tree Blog

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

File Permission Meanings Stack Overflow

Ownership And Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Top 48 Linux Interview Questions Answers Updated

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Linux Command Chmod Vichhaiy Welcome

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

100 Mejores Imagenes De Linux Informatica Linux Computacion
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Scripts Or Directories Linux Accounts Only

Unix Permissions

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Can We Set File Permissions To 775 By Using Umask In Linux If Yes What Would The Umask Be And How Will It Be Calculated Quora
Linux Permissions Explained Linux Hint
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
Ask Klaus Linux Magazine

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Lpt Memorize Chmod Values By Using A Truth Table Imgur

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux Unix Permissions Amal Mammadov

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Managing Linux Permissions

System Integrity Using Files Permissions Processes Root And Sudo Teklimbu S Weblog
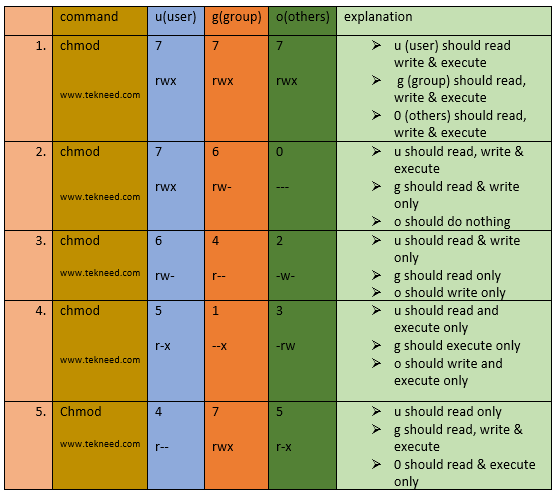
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqzjwejtv9wexgnjg6wrv4scdirjlf8ko Drmhmencfjup H30u Usqp Cau

Suse Linux Enterprise Desktop Administration Chapter 9 Manage Users Groups And Permissions Ppt Download
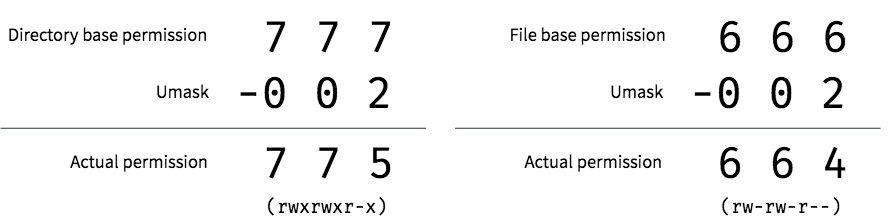
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Chmod Wikipedia

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
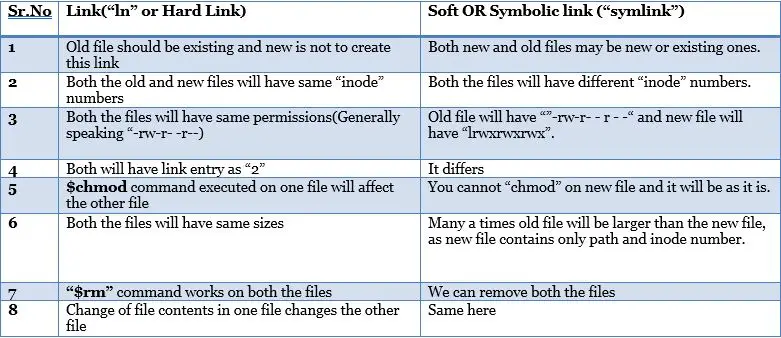
How To Create Hard And Soft Symlink Links On Linux Systems

Understanding File Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
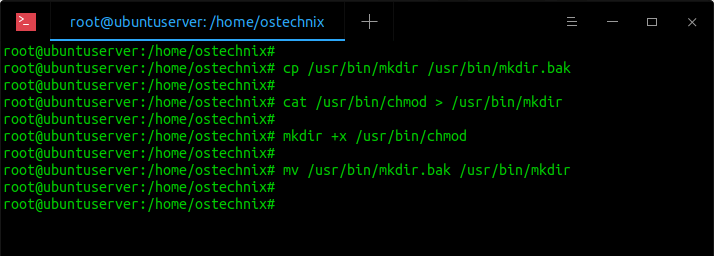
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen
Srgoc Linux

Ownership And Permissions

File Chmod Infographic 001 Png Linux Help
Unix Linux Filesystem Permissions 101
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy
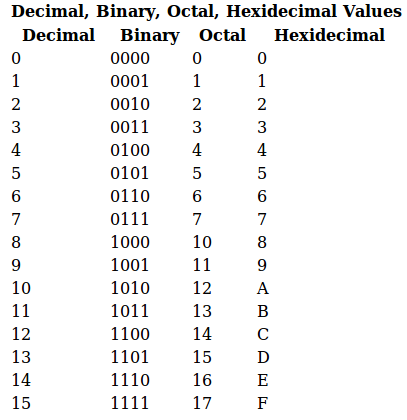
Learn Oracle Concepts Unix Permissions Table

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gcshaj Y1vkiemycwkpaupncp4unfaocvspjkpccsqvubbllyat0 Usqp Cau

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean
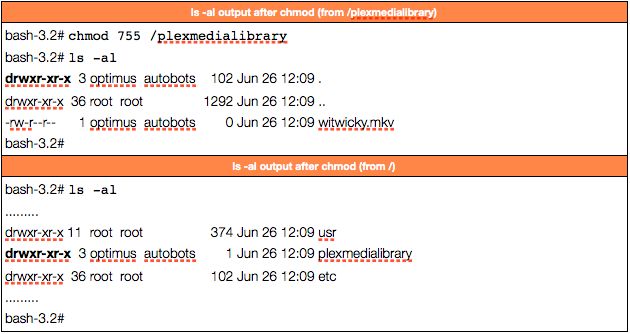
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Unix Permissions Amal Mammadov
Verizon Droid Turbo Has Been Rooted Page 2 Droidforums Net Android Forums News



