Chmod Example Recursive

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Chapter Linux Basics Acknowledgements This Presentation Was Prepared By Banyat Settapanich Bahran Madaen This Presentation Will Be Updated Later Ppt Download

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
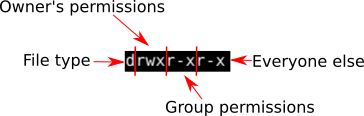
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students
For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:.
Chmod example recursive. The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering. From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains).
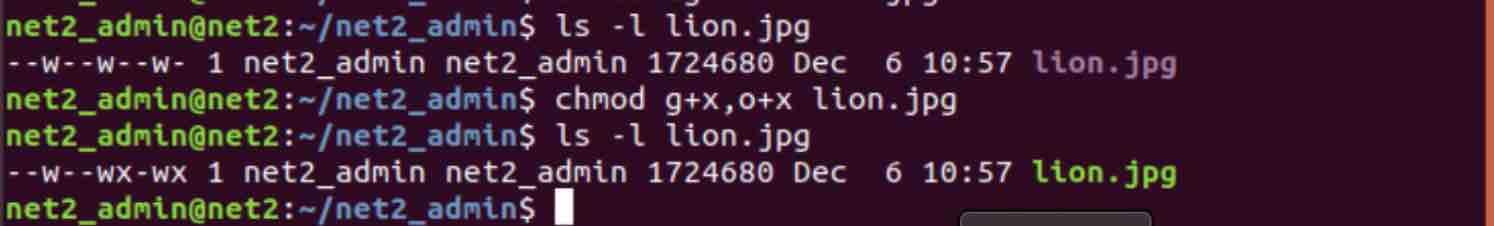
We can also change permissions for file contained in a specific directory with a single command. Perform chmod recursive with -R or --recursive. Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write.
The owner receives full access rights (7);. To make the chown command recursively operate on files and directories, use the -R command-line option. $ chown -R <owner> <folder_1> <folder_2>.
So the above command will copy the owner and group information from file2 to file1. Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number. Donotprint /donotprintThe find command can be used to find files and directories.
Or you can set the permissions recursively. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma). Use option -R to change the permission recursively as shown below.
Note that this function has one argument for directory permissions and one for file permissions. The command chmod a+rwx is equivalent to chmod ugo+rwx. As mentioned by Rinzwind here is a better way of accomplishing what you want.
Arbitrary code from (sometimes) arbitrary fora pasted into arbitrary terminals, by a guy who wants to "chmod 707 -Rv ." except for two directories sourced from "some guy" with 2 posts?. Chmod OPTION… –reference=RFILE FILE…. The net is dangerous enough.
It means giving read/write/execute permission to file owner but revoke every permission from group and everybody else. The chown command can be used to change user and group permission. To change the owner and group of all files in the directory /tmp/src to owner john and group build:.
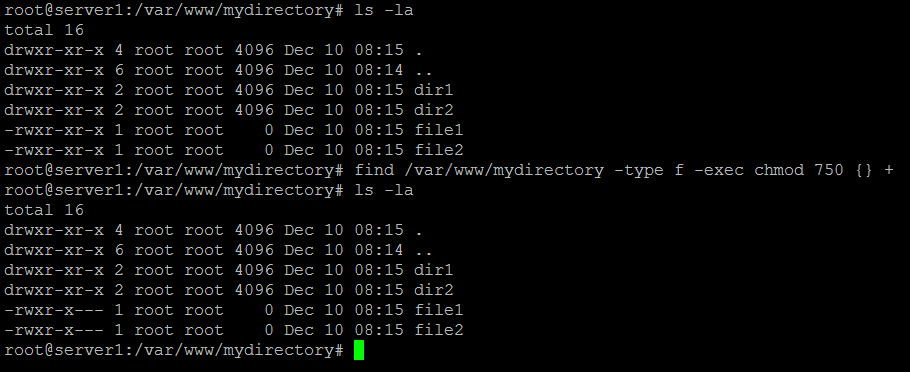
One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. Chmod -R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type:.
-type f -exec chmod 750 {} +. $ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions.
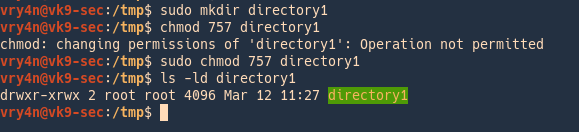
$ chmod -R -@ '' -@ '*' S+a directory1. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility.
Examples of chmod command /chmod recursive. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. Prompt> chmod options permissions files The word "chmod" should be entered all in lowercase letters.
It has -R or –recursive option that change files and directories recursively. Includes objects stored in subdirectories) and force (which ignores errors and continues applying chmod). The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system.
In the event that a symbolic link is included, chmod includes the file or files specified in the link. Chown -R new-owner:new-group directory. $ chmod -R 755 directory-name/ 7.
Chmod --changes|-c {--recursive|-R} {PATH}. Options can be:-R, set permissions recursively-f, "forced" or silent mode-v, "verbose", show information for every file processed. Descends directories recursively, changing the ownership for each file.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Use -R, as shown below to provide the recursive privileges for the directory and sub-directories (including the files in it). $ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthday.cgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:.
In case - while dealing with directories and subdirectories - you want to make recursive changes, you can do so using the -R command-line option. $ chmod --reference=file1 file2 6. $ chmod -R 744 examplefolder The following applies to all files and subfolders in the directory ‘examplefolder’:.
(G)roup can read, can write and can execute. Changing permissions with chmod. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command.
Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. The syntax to modify the file and directory permission recursively:. Example 25 Recursively Descending Through a Directory Hierarchy.
To do this recursively you can use the -R flag and the -v flag to get a verbose output of the action. If you want to change the permissions of only files located inside specific directory then you will need to apply conditional file permissions recursively. Avoid changing any file permissions on directories and files set up by.
For example, I am going to apply 777 permission to a folder and all of its content using the following command. When assigning permissions to directories, use the -R flag to recursively assign permissions to its files and subfolders. To change the permissions of a directory, we run:.
Chmod examples using octal mode :. Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system.
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. User can read, write, and execute;. If you specify both the -hflag and the -Rflag, thechmodcommand descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link isencountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is not changed.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode"). The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
Several symbolic methods are equivalent;. Chmod permission directory name To change the permissions of a directory with its files and sub-directories recursively, we run:. For recursive chmod'ing both files and directories in one step you can use the function below.
All you need to do is to run the chmod command with Recursive option -R. The following example recursively descends through a directory hierarchy, and sets all system attributes of all named attribute files, the ZFS file operands, as well as of the directory itself:. To modify the permissions of each and every file and folder in a provided directory at once, use sudo chmod with -R:.
If you specify the -hflag, the chmodcommandprevents this mode change. You can use chmod with the X mode letter (the capital X) to set the executable flag only for directories. Apply the permission to all the files under a directory recursively.
How to make chown operate on files and directories recursively?. Following are some examples:. Chmod options-R – Recursively change the permissions in the file under the directory.
The letter a is a shortcut to assign permissions to all users. The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:. Like many other Linux commands, chmod has a recursive argument, -R, which allows you to operate on a directory and its contents.
Adding execute permissions to others. We can also use Octal numbers for chmod chmod 700 file1 :. In this example, file2’s permission will be set exactly same as file1’s permission.
Sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www Before using either of these, really consider if you want your filesystem to be so accessible. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. In this way you can apply the 'x' permission on directories, and skip it on directories.
Chmod --reference=file1 file2 Recursively Change the File’s Permissions # To recursively operate on all files and directories under the given directory, use the -R (--recursive) option:. Chmod 775 Chmod 775 (chmod a+rwx,o-w) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. The aforementioned command will make the group ownership of file1 same as that of file2.
The most common options include verbose (-v or –verbose;. Removing execute permissions to a user. In the example below the executable flag is cleared and then set for all directories recursively:.
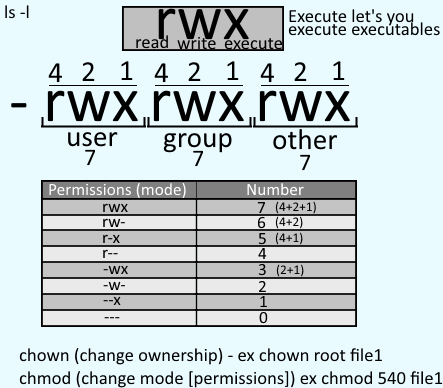
If all your files and directories are under one parent directory then you can directly use chmod -R <dir_name> to assign the permission recursively. $ chmod 755 sysadmin.txt Example 2) Recursively assigning permissions to directories. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa).
Change the user or group ownership of any directory recursively. You can do the same in symbolic mode. In the next post we will see more about chmod options and examples such as change file/folder permissions recursively, SUID, SGID and Sticky bit.
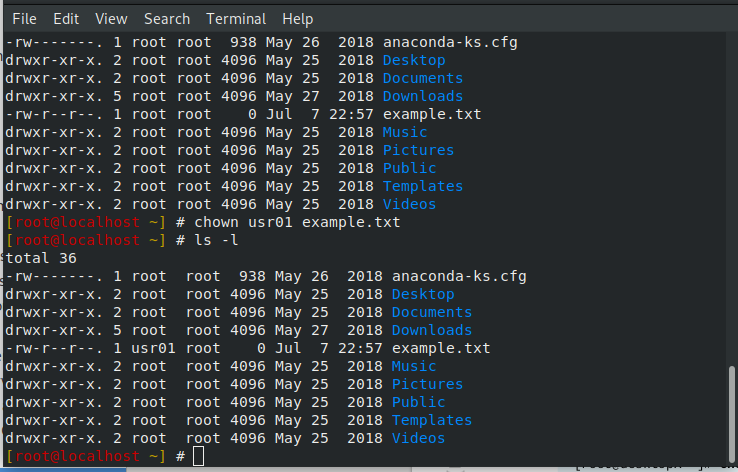
The easiest way to use the chown recursive command is to execute “chown” with the “-R” option for recursive and specify the new owner and the folders that you want to change. As the owner, jim can use the chmod command to permit or deny other users access to program.c. Group members and other users only have reading access.
Sudo chmod - Rv 755 /path/destination See here and here for further reading into. Chmod -R o-r *.page Numerical Shorthand. Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:.
Chmod command Examples In this section we will show you how to change permissions on directory and sub-directories with examples. There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. Sudo chmod -R 755 Example.
One example is chmod u=rwx,go=rx,o+t. To change file access permissions you need to use the chmod command. How to ask chgrp to make changes recursively.
It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory. $ chmod 755 -R directory_name $ chmod 755 -R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation. Explore your self on how to use other options.
Chmod g-x file1 :. The chmod command specifies which class or classes (user, group, other) have access to the. (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute.
Shows the items you’re processing), recursive (-R or –recursive;. So the line you search for is:. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022.
Cd /var/www/mydirectory find. The following example command changes access rights recursively for all sub-directories and files as well as for the folder itself:. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
Chmod syntax for symbolic values chmod OPTION MODE1,MODE2 FILE. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php. A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1.
The following `chown` command with -R option will change the user ownership to ‘root’ and group ownership to ‘testing’ for all the files and folders under ‘code’ folder. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):. First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission.
Chmod -R permission directory name For example, to set the permission to 755 recursively to /var/www/ diirectory execute the command. $ chmod -R g+rwx /u01. To change the owner of the file program.c:.
Read by owner only $ chmod 400 sample.txt Read by group only $ chmod 040 sample.txt Read by anyone $ chmod 004 sample.txt Write by owner only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by group only $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only. Syntax and examples of the shell chmod command (telnet or SSH) Syntax of the chmod command is the following:. If we had wanted to include files in subdirectories, we could have used the -R (recursive) option.

Common Bash Commands

10 Ways To Use The Chown Command With Examples Foss Linux
Linux Cheat Sheet By Deleted Download Free From Cheatography Cheatography Com Cheat Sheets For Every Occasion

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Accessing Internal Data On Android Device Codeproject

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Chmod Wikipedia
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Chmod 7777

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
Chmod Syntax

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Unix Commands Command Line Interface File System

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Linux Permissions Deep Dive Part 1 By Runcy Oommen Medium
Linux Cheat Sheet

Hdfs Commands Hdfs Permissions And Hdfs Storage Managing Hdfs Through The Hdfs Shell Commands Informit

Extropia Tutorials Introduction To Unix For Web Technicians The Chmod Utility

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line
File Permissions In Linux Dzone Open Source

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
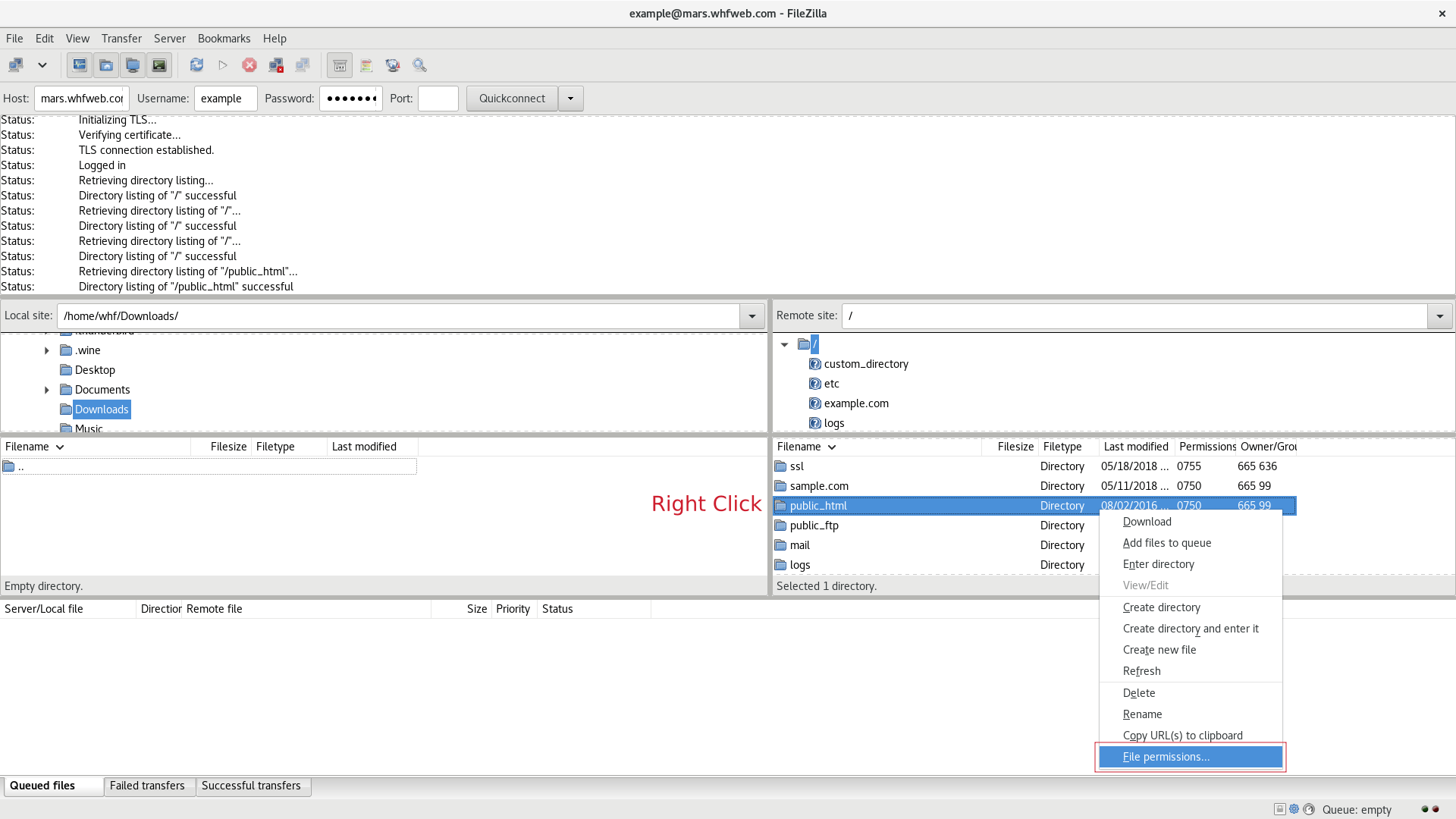
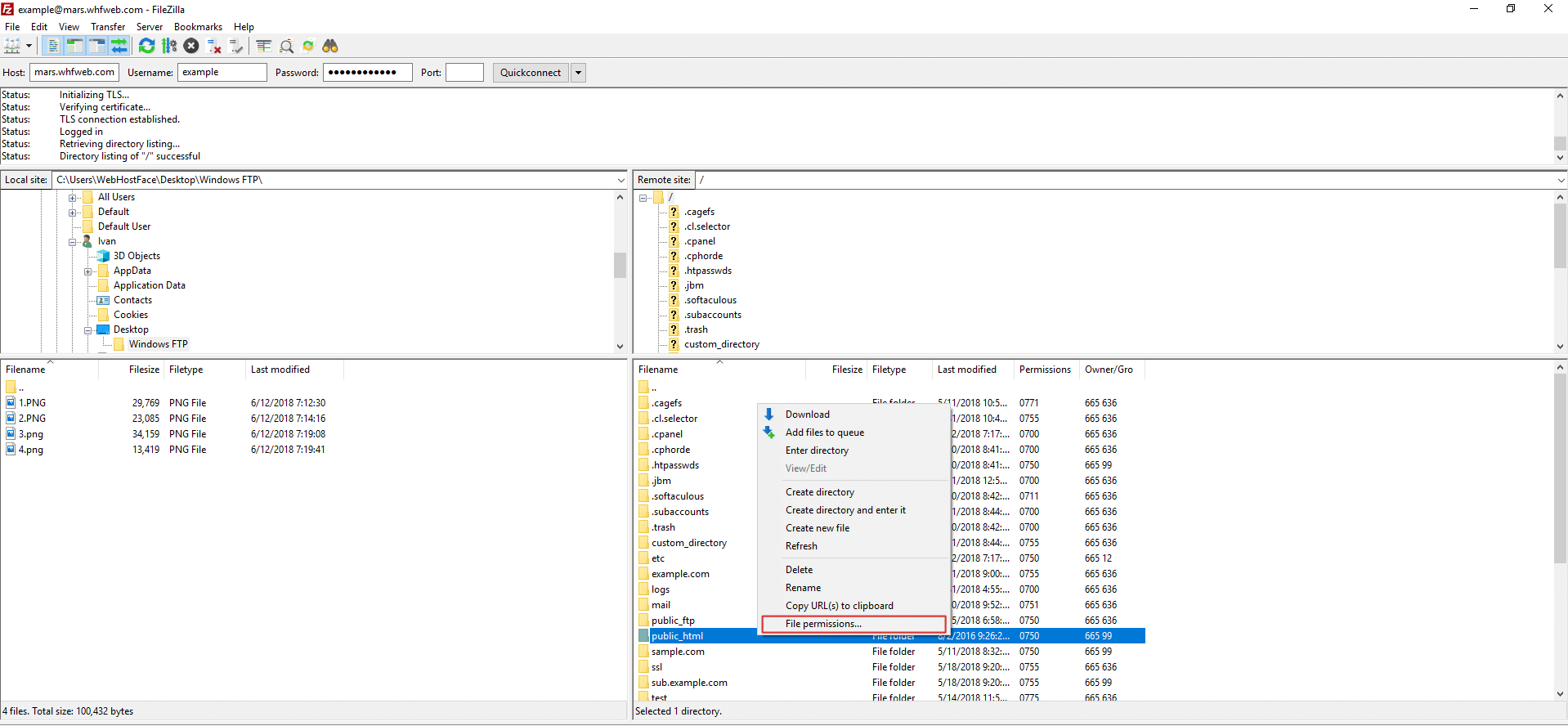
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting
12 Frequently Used Hadoop Hdfs Commands With Examples Usage Dataflair
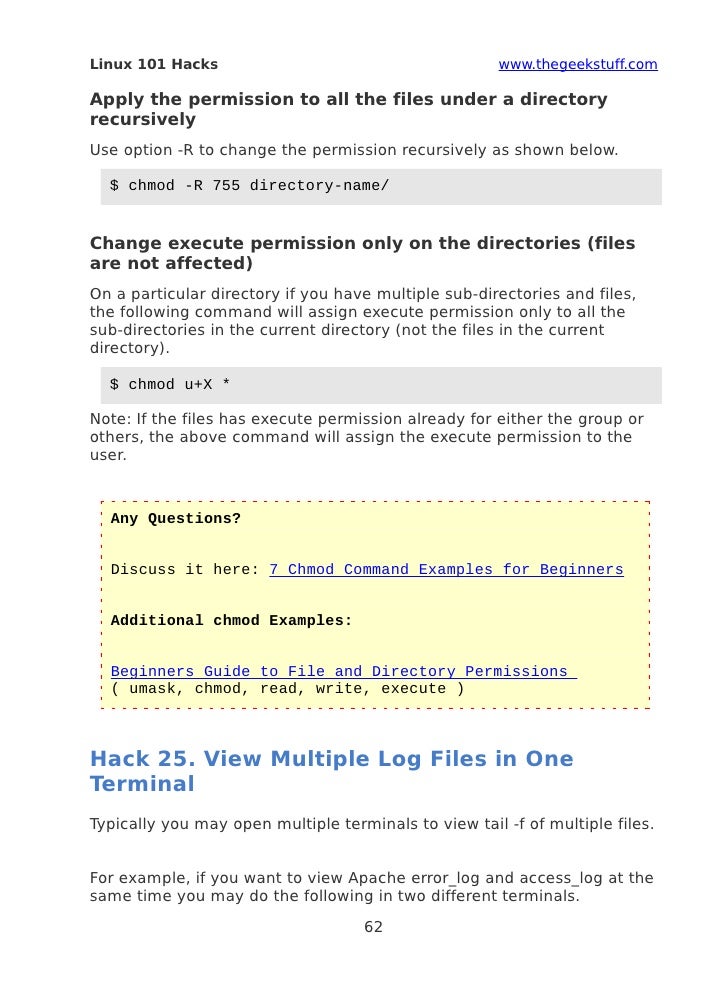
8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com

Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather

Chmod Command Tutorial How To Recursively Set Permissions In Sub Folders
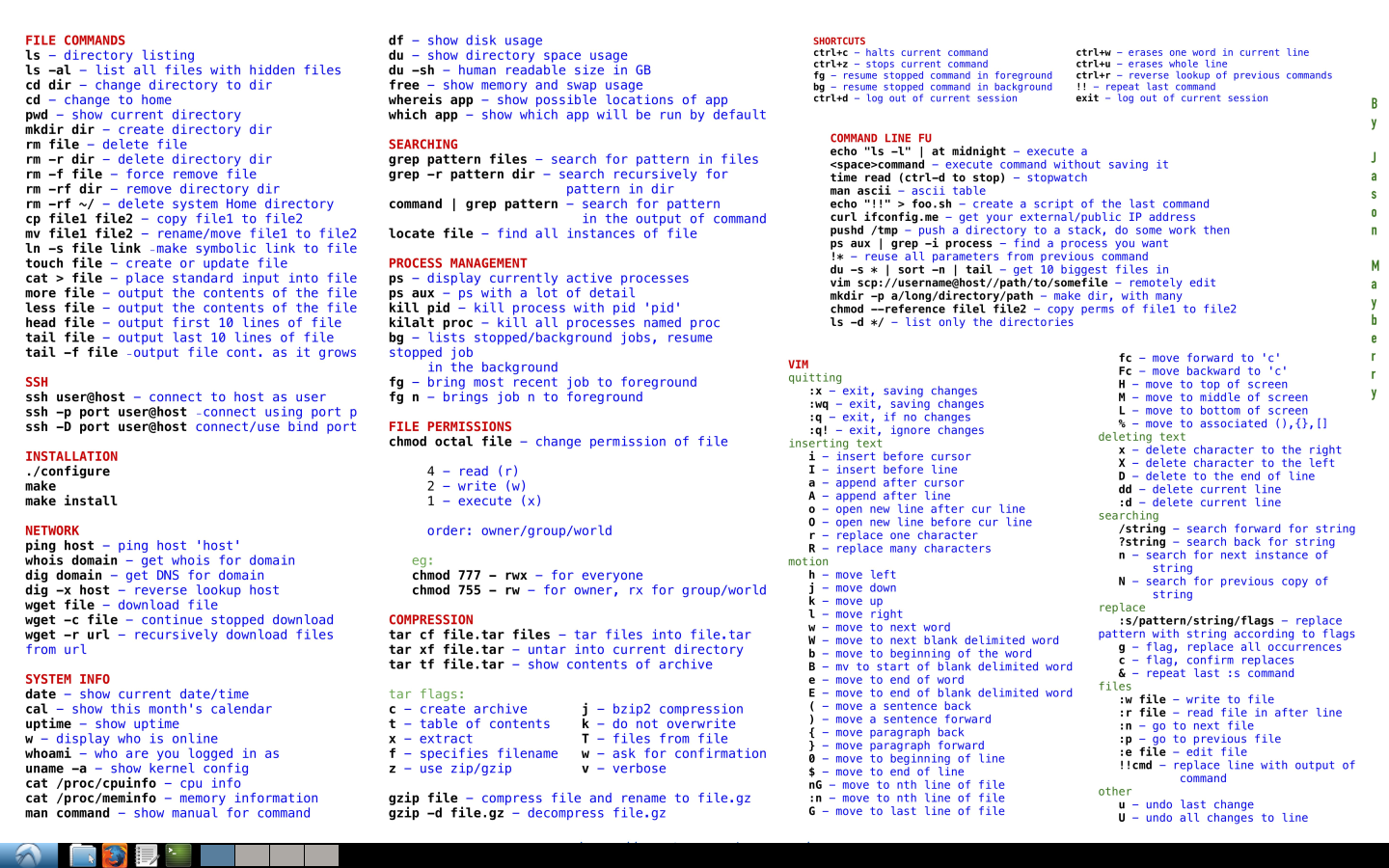
New Bash Linux Cheat Sheet Wallpaper Download Free 40 X 3050px
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau

How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners

How To Apply Chmod Recursively With Best Practices Examples Golinuxcloud

How To Change File And Directory Permissions With Chmod Recursively Poftut
File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

Need Help With This Question Please For Coding Pl Chegg Com
Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example

Chmod And Chown For Wordpress

Course 102 Lecture 14 Users And Permissions
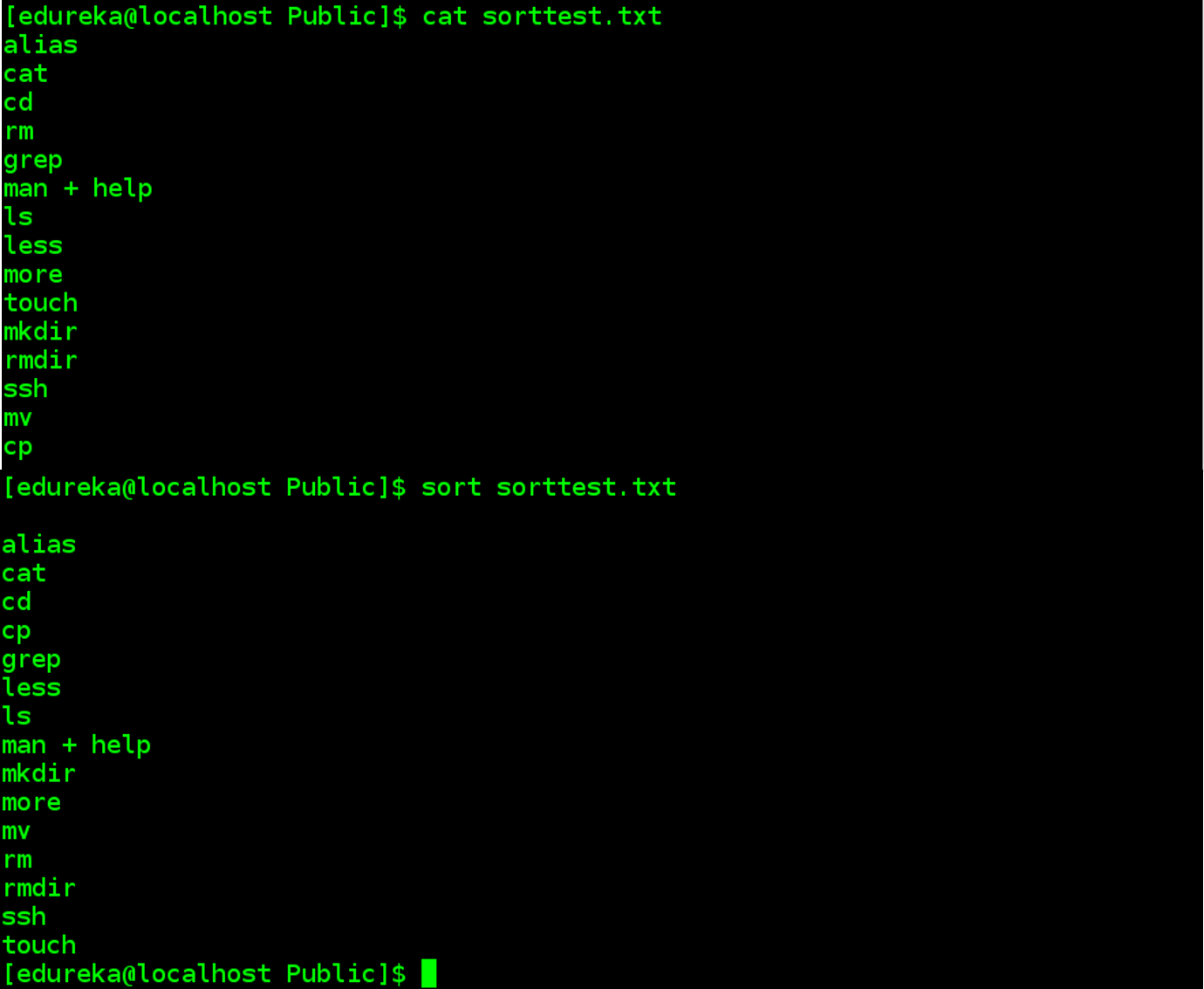
Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka

A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More
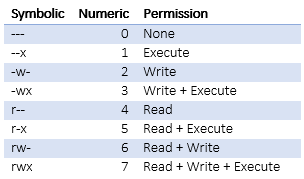
Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux
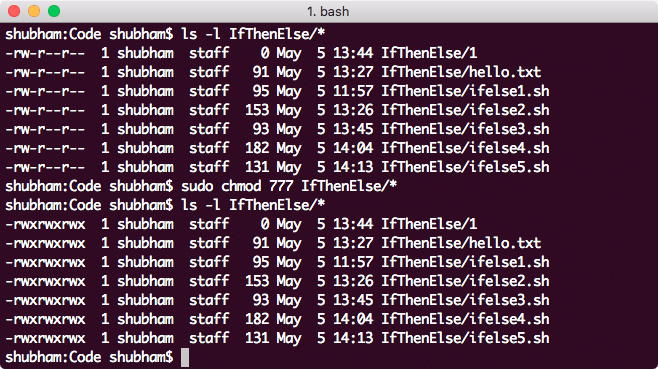
Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
2

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Linuxconfig Org
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Hdfs File System Commands Hadoop Online Tutorials
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
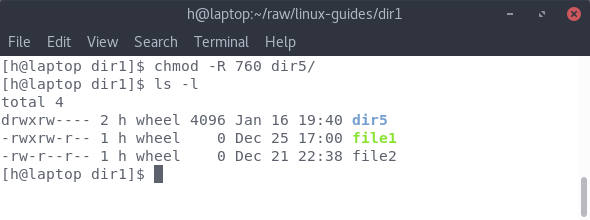
Linux Command Line Tutorial 4 File Permissions Steemit
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Basic Linux Usage

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Golinuxcloud

How To Change File And Directory Permissions With Chmod Recursively Poftut

Linux Commands Chmod

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Organic Traffic Service

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

14 Permission And Modification Times

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Help Examples How To Use Chmod In Linux Ionos
Linux Chmod Tips

Lab Diary Entries Professional Skills Cs133 Warwick Studocu

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

Chmod Folder And Subfolder

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Perl Chmod Command How To Set And Remove File And Directory Permissions Udemy Blog
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Chang Min Park



