Chmod Numbers Meaning

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Tryhackme Episode 3 Learn Linux By Whdvl Sep Medium
Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Ownership And Permissions
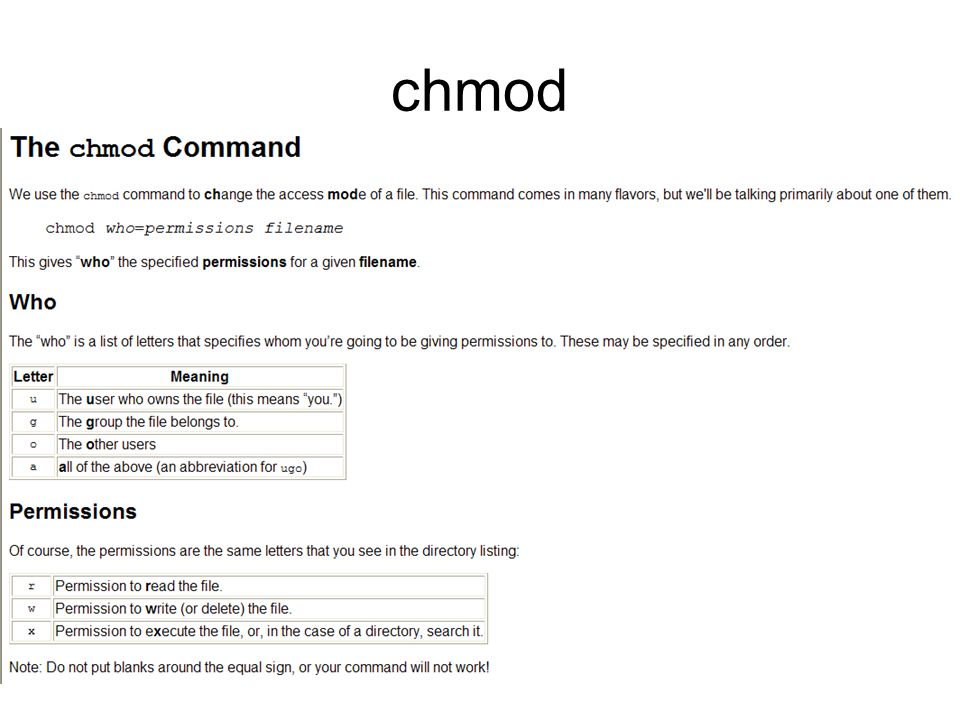
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.

Chmod numbers meaning. The numbers are a binary representation of the rwx string. (O)thers can't read, can't write and can't execute. In this examples we will enable group execution of file app.sh $ chmod g+x app.sh Change File Mode For Other.
766 is the mode we are changing the directory to, it means that the directory is readable and writable by WordPress and any and all other users on your system. What is CHMOD and what do the numbers mean?. When the 4 digits number is used, the first digit has the following meaning:.
Chmod u=rwx filename If you want an easy way to know the Linux file permission in numeric or symbolic mode, you can use this chmod calculator. (O)thers can read, can write and can't execute. Chmod +rwx “filename” chmod-rwx “directory name” Changing permissions for the group owner and other members.
This person cannot read, write, or execute the file 1 = execute only. This video attempts to explain what the "chmod" numbers mean that are often used but never explained in guides and installation instructions. Using flags is an easy and short form to set user permissions.
All, As first i searched in google but no result. And = causes them to be. Base 8, digits 0 - 7.
000 0 001 1 010 2 011 3 100 4 101 5 110 6 111 7. Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:. Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode.
If the first digit is 0 it can be omitted, and the mode can be represented with 3 digits. If you come across a rather cryptic word “lrwxrwxrwx” when listing files and directories, here’s how you can interpret it. Change permission for all roles on a file/directory.
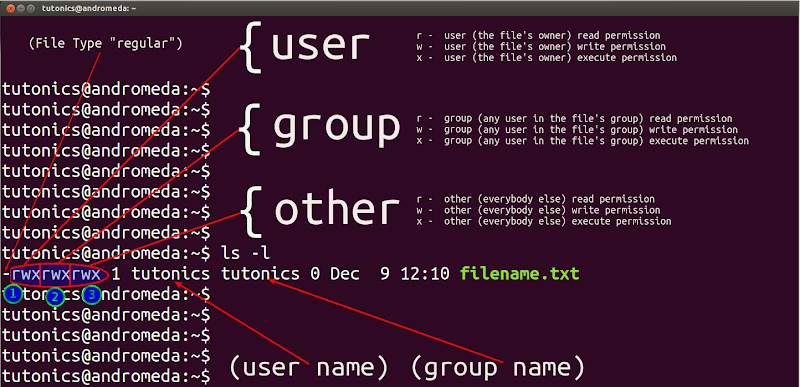
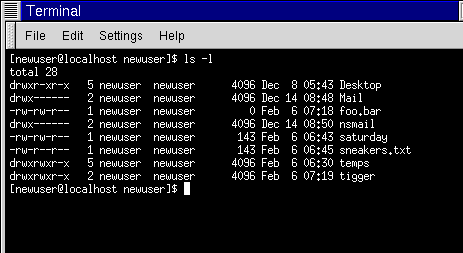
$ sudo chmod OPTIONS numeric_value filename. The two columns next to this number (drwxr-xr-x 3 dd users) represents the owner and group of the file. To find the permissions for a particular file or directory, specify the name of the file in the ls command like.
The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. Well, each of the three numbers corresponds to each of the three sections of letters we referred to earlier. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument.
An example use of the chmod command would look like:. If you use 600 it equals 0600. Symbol Meaning u user g group o other a all r read w write (and delete) x execute (and access directory) + add permission-take away permission # remove read write and execute permissions # on the file biglist for the group and others chmod go-rwx exam.pdf # give read and write permissions on the file.
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. It stands for change mode. The middle digit represents the permissions for the group members.
-R means recursive addition of permission to each file/directory which is mentioned. The first octal digit sets the setuid, setgid and sticky bits (see this article for more details on setuid/setgid). Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.
To quote the man chmod:. If this is your first visit, be sure to check out the FAQ by clicking the link above. Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation.
In other words, the first number determines the owner permissions, the second number determines the group permissions, and the third number determines the other permissions. We can use g group before the plus in order to enable group execution right of the given file. Chmod 775 / path / to /file Hopefully, this article can help you understand better about the file permissions in Unix system and the origin of the magical number “777”.
Chmod (change mode) is a Linux command used to set Read, Write and Execute permissions for different types of users. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:. Please note that chmod 777 filename is the equivalent of chmod 0777 filename in this example.
The number “775” is to provide permission to the file. This command is similar to the first one, all you need to add in here are “o” for other users and “g” for groups. $ chmod u+x app.sh Change File Mode For Group.
No changes = 0;. The leftmost digit (the "2") is optional and defaults to zero if not specified. - causes them to be removed;.
The numeric value can take 3 or 4 numbers. The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers. Write the permissions you want the file to have.
The -R flag means to apply the change to every file and directory inside of wp-content. Group permissions – since each file belongs to a particular group, this. It is a set of 12 bits that make up 4 distinct permission fields of 3 bits each, also called tri.
This is known as symbolic mode. 777 or -rwxrwxrwx - for files that are written to by all. You add the numbers to get the integer/number representing the permissions you wish to set.
To chmod a file means to set certain permissions. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. $ chmod u+x filename 2.
So, the equivalent would be to do a chmod a+rwx filename, then chmod g+s filename.The chmod info page does explain this in more detail. If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file.
To make your life easier, write the permissions grouped into sets of three letters. Chmod g-s Security Risks. Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system.
755 or -rwxr-xr-x - directories are usually given this value. The octal number used for the code chmod/code command is not an integer. With chmod +x you set the executable bit for all - the owner, the owner group, and the other users.
Here’s how it works:. The sums of these numbers give combinations of these permissions:. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
You will need to include the binary permissions for each of the three permission groups. Click the register link above to proceed. When we use the chmod command later on, you’ll see that you can change the permissions using either symbols or octal numbers.
We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. As you know, file permissions in Unix are traditionally provided using 3 levels:. To start viewing messages, select the forum that you want to visit from the selection below.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa). Let’s now delve and see different examples of chmod command. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it.
The setuid bit is indeed quite useful in various applications, however, the executable programs supporting this feature should be carefully designed so as to not compromise on any security risks that follow, such as buffer overruns and path injection. 15-05-19 In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe.
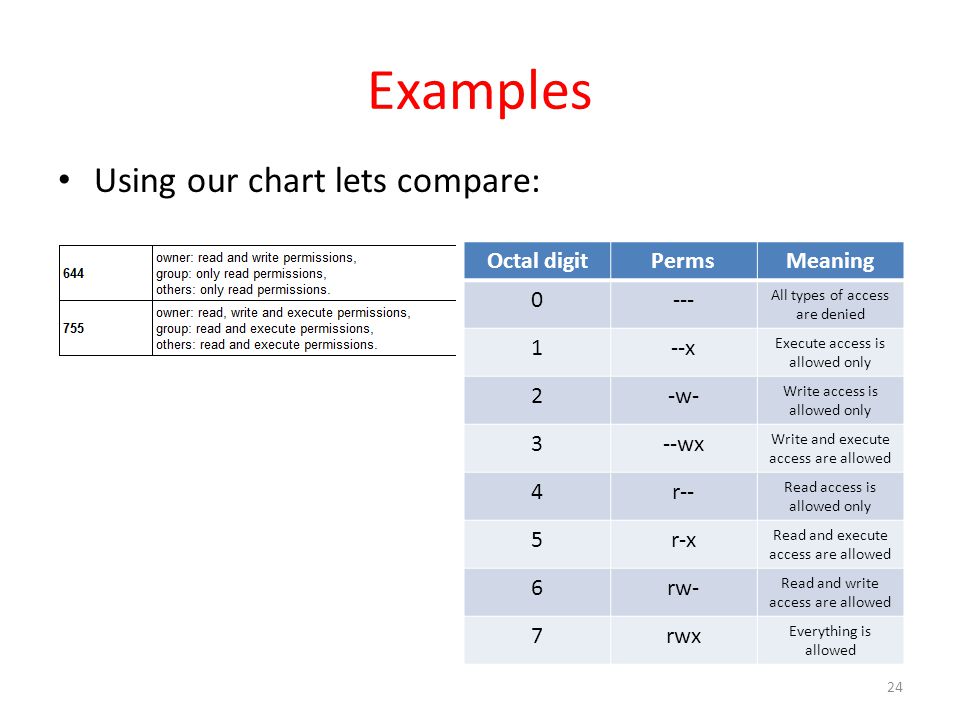
$ chmod u-rx filename 4. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The setting 644 is relatively safe, as it provides "Read" and "Write" access to the owner, while limiting the rest of the public to "Read Only" access.
Chmod 666 Chmod 666 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-x,o-x) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can't execute.(G)roup can read, can write and can't execute. The numeric mode 0755 is the same as 755. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
User (file owner) permissions – specifically, permissions for the user currently setup as the file owner;. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute. Typical Chmod Permissions Values 644 or -rw-r--r-- web pages and images viewed by surfers.666 or -rw-rw-rw- - log files or pages to which are written.755 or -rwxr-xr-x - perl scripts to make them executable.
0 = no permissions whatsoever;. But often, only three are used. The difference is what permissions get set and which mode you use to set them.
"2775" is an octal number that defines the file permissions. $ chmod u+r,g+x filename 3. From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Chmod -R 777 directory/File 777-Giving Full permissions as READ , WRITE and EXECUTE to all users. Octal 2 means to set group ID on the file.
However, in most cases, 3 numbers are used. The next three digits have the same meaning as when using 3 digits number. You may have to register before you can post:.
The operator + causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file;. The digits in the "775" portion define the permissions for the file owner, file group, and everyone, from left to right respectively. So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols.
The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments.
Each number can have one of eight values ranging from 0 to 7. Numerical Shorthand Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number. Add multiple permission to a file/directory.
Remove permission from a file/directory. Chmod ugo+rwx or chmod u-rw or chmod u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx or a=rwx (a means all) At the risk of scaring with a short shell script, it is possible to view all the permissions minus the sticky bit, the SetGUID bit, and the SetUID bit using some loops:. Want to know what the numbers in chmod mean?.
Yes, I did call it "decimal notation", this is. So to set a file to permissions on file1 to read _rwxr_____, you would enter chmod. About Chmod # About Chmod chmod is a unix command that means “ ch ange mod e” on a file.
Chmod 770 (chmod a+rwx,o-rwx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. Chmod g+s To remove the setgid bit, use the following command. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively. Up to this point, we’ve been setting the mode with letters. The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner.
This article(I hope) puts it SIMPLE, if you want to learn the theory, also visit the links in the end. Chmod by the Numbers. It turns out that you can also set the mode numerically.
I am having a directory with permision drwxrwsr-x i want to create a new directory with same permision. There are four OCTAL (07) digits, which control the file permissions. Example 1) Assign permissions using numeric notation.
The options of chmod are as follows:. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
The numbers for code chmod/code are octal. Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. To understand this further, we should first break down.
When setting permissions using the numeric style/notation, use the syntax shown below:. If a vulnerable program runs with root privileges, the. The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons.
The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. The three digits 755 and the order they are in determine what users are set which permission. The 11th character is a number that represents the number of hard links for the file and is not related to permission for a file.
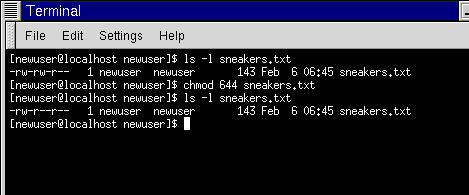
By default, all files uploaded to the server automatically have permissions set to 644. Also i searched in the forum as well. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Following example removes read and write permission for the user.
777 or -rwxrwxrwx - directories that have files created inside them.

14 Permission And Modification Times

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
Chmod 0400 Means

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Write Access Chmod Permissions
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
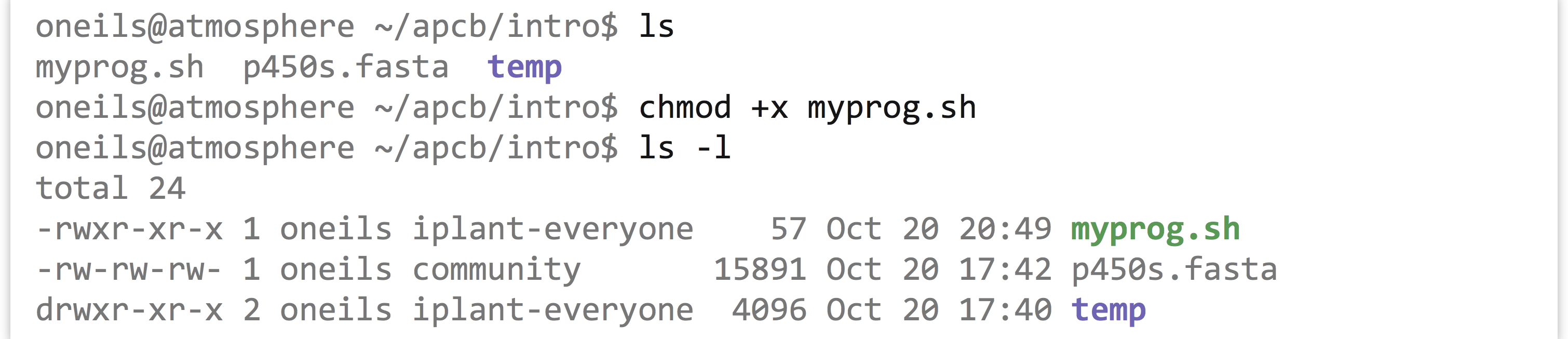
Permissions And Executables A Primer For Computational Biology
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
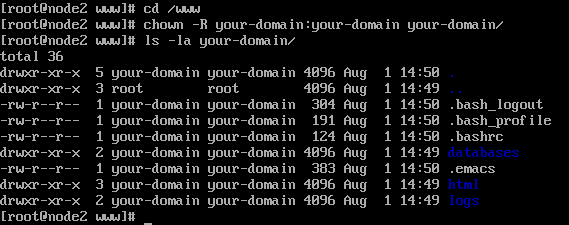
Chown Command In Linux Unix Explained With Examples The Linux Juggernaut

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

What Does Chmod Mean In This Context Macrumors Forums

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod Wikipedia

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book
Q Tbn 3aand9gct7wt7gzhduflbfyn8phh8frjezj69hwxbeqqg4p T9 V8epo92 Usqp Cau

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Unix Permissions

Linux Command 9 Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Linux From Beginning

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

10 Try Read Try C Again Using Cat Attach A Scr Chegg Com
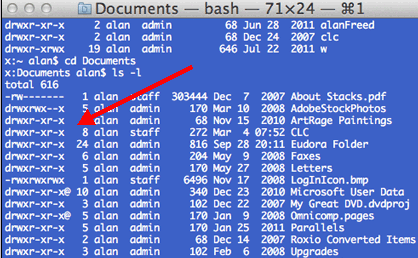
Chmod Unix Article About Chmod Unix By The Free Dictionary
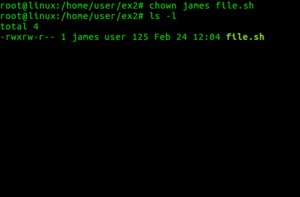
Chown Wikipedia

Chmod Files And Permissions Utskyring Og Leidbeiningar Spjallid Is

Ownership And Permissions

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
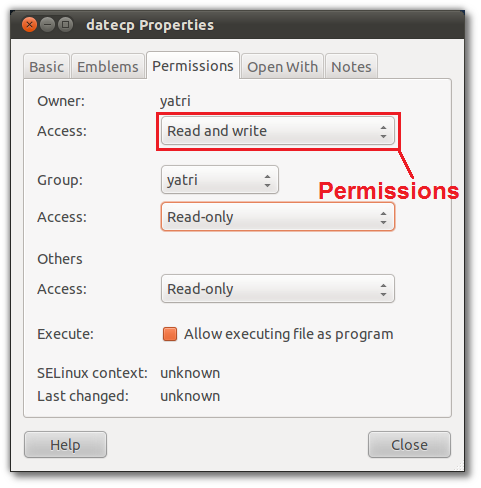
What Is Chmod 777

Unix Tutorial Five

Understanding File Permissions

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Ownership And Permissions

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
2
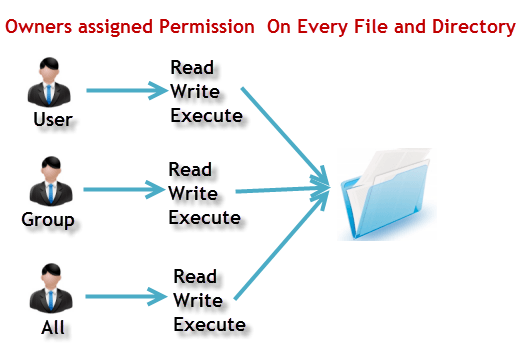
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
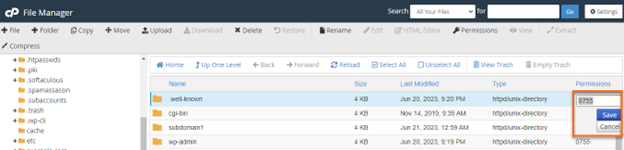
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

What Is Umask And How To Use It Effectively Liquid Web

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
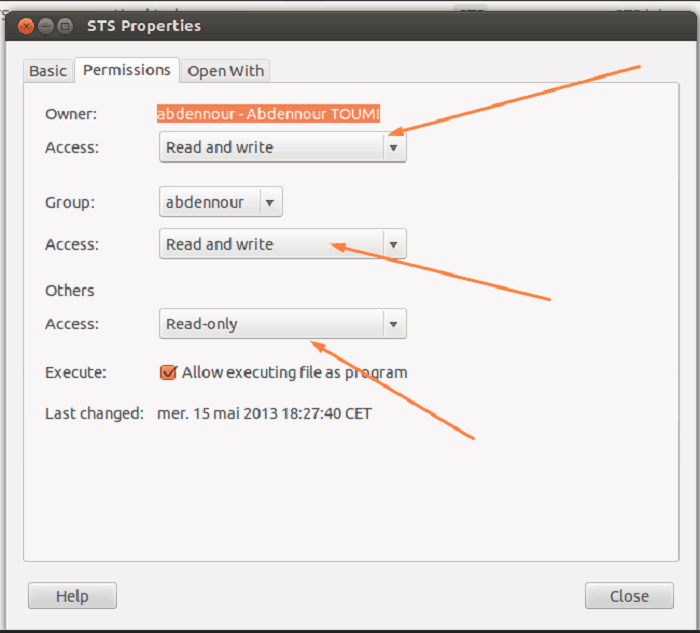
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Ownership And Permissions
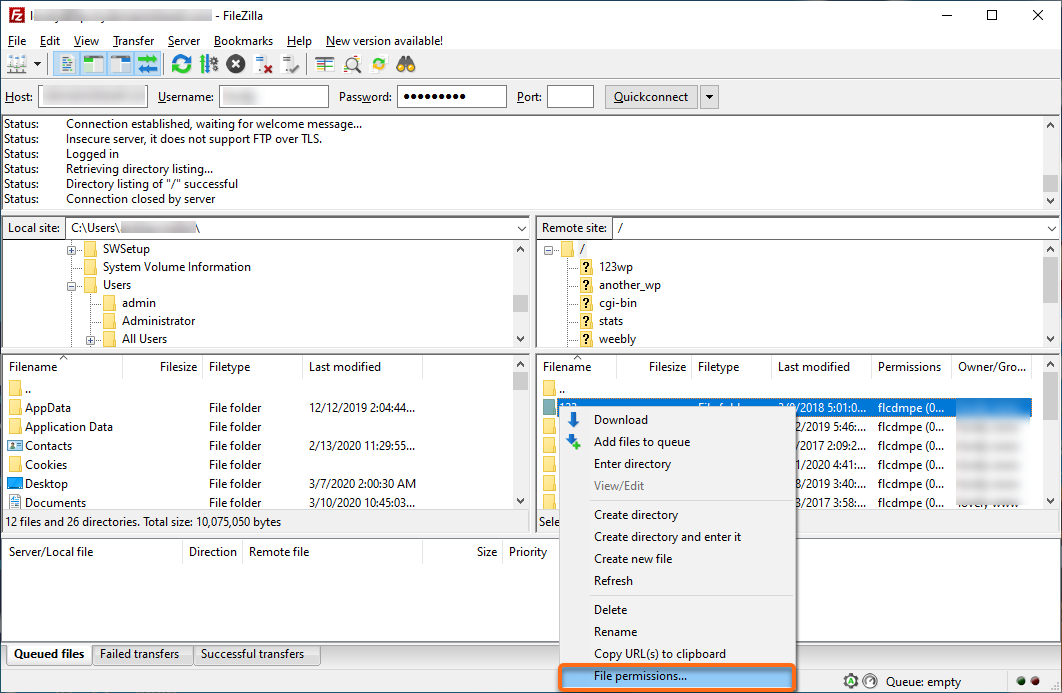
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

10 Try Read Try C Again Using Cat Attach A Scr Chegg Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

Wordpress File Permissions A Guide To Securing Your Website

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange
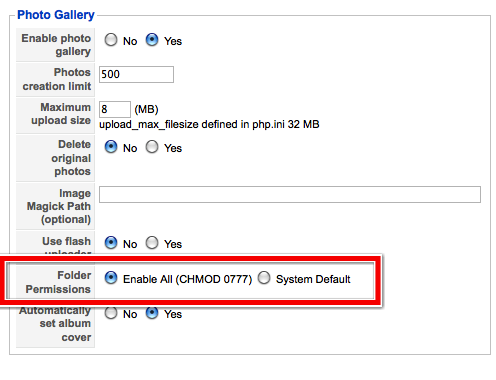
Brian Teeman Jomsocial You Cannot Be Serious Chmod 777

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Ownership And Permissions

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Chmod Command 1 Vichhaiy Welcome

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
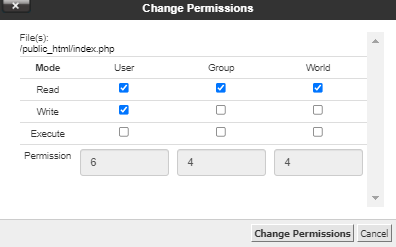
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Solved Part 3 Permissions For Files Follow The Instructi Chegg Com

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
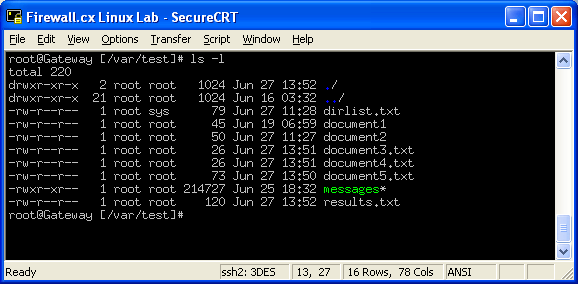
Linux File Folder Permissions



