Chmod Permissions

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Write Access Chmod Permissions

Chmod Calculator Takes The Hassle Out Of Directory Permissions Techfruit
One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive).

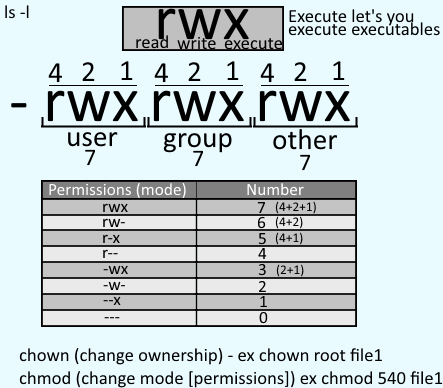
Chmod permissions. To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod(change mode). The use of an equal sign (=) wipes all previous permissions for that. There are two ways to represent the MODE:.
Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. Chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. There are two basic ways of using chmodto change file permissions:. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”.
Chmod 444 file - Allow read permission to owner and group and world chmod 777 file - Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for. To determine the mode (or permission settings) of a particular file, use the command `ls -lg filename'.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. 4 = read permissions. The permission scheme described above also applies to directories.
$ chmod 444 sample.txt Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions.
(O)thers can read, can't write and can't execute. Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. Read (r), write (w) and execute (x) permissions.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. This is thanks to interopability, as any read or write commands to Windows files are routed through your Windows user permissions. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable.
Sudo chmod g+w myfolder to add the write permission to the group. Set Executable Permissions to Script Step 5:. Take a look at this example:.
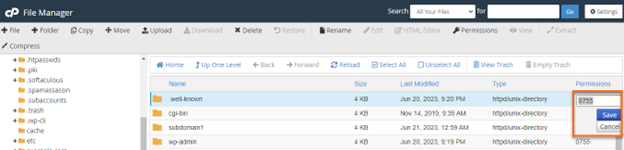
There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members. This mechanism is based on two parts i.e.
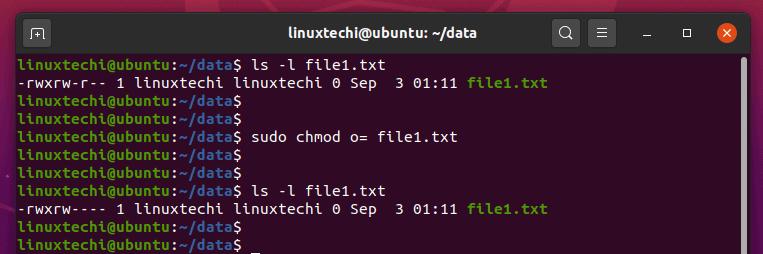
Turns on a permission. Writing a Sample Script Step 3:. For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r--execute:.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. There are 3 types of access level permission which unix gives. It is also used to change special mode flags.
The u flag sets the permissions for the file owner, g refers to the user group, while o refers to all other users. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
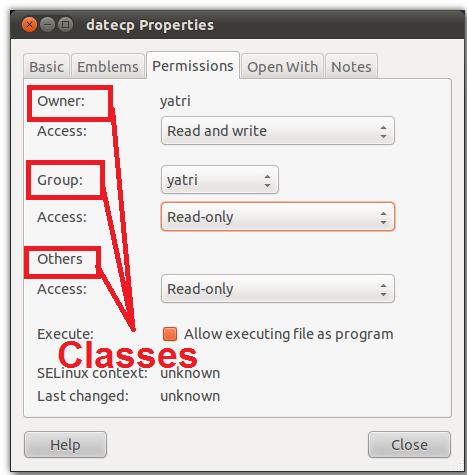
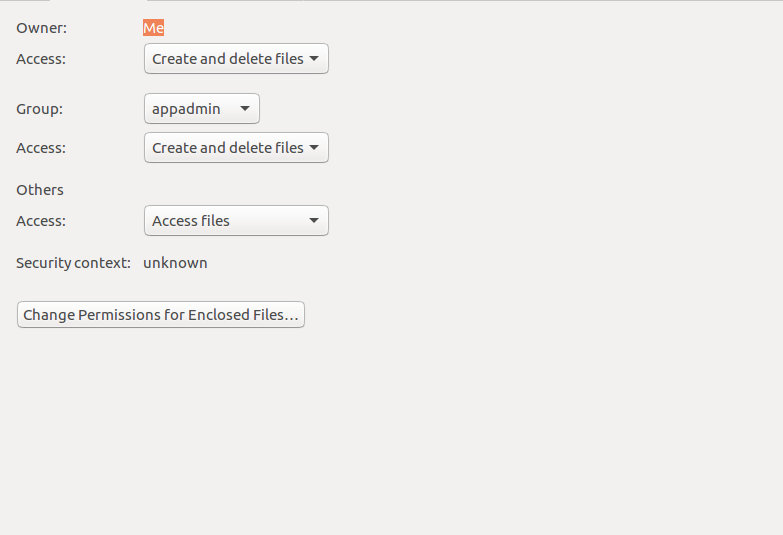
Chmod can be used only by the file owner or a superuser. W - Allows files within the directory to be created, deleted, or renamed if the x. Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the "user"), members of the group who owns the file (the "group"), and anyone else ("others").
The possible values are:. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 754 (chmod a+rwx,g-w,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
It’s also possible to add permissions incrementally. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions.
Sudo usermod -a -G groupname username and then execute. The second number specifies permissions for the owner;. The chmod (CHange MODe) command is used to change permissions for a file or directory on a Unix machine.
For a directory, whoever has `read'. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. This is illustrated in the calculation below.
Changing File Permissions - Chmod The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. If you want to use an option, you have to place it right after the chmod/chown command. The references are shorthand (u, g, or o) for each class.
Here we are going to explain to you chmod 775 , 755 & File permissions. Namely Classes and Permissions. =turns on the specified permissions and turns off all others.
2 = write permissions;. Chmod() automatically clears the S_ISGID bit in the file's mode bits if all these conditions are true:. Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission).
# perl -e 'chmod 0755, "/usr/bin/chmod"' As you can see, this is a trivial problem which can be easily resolved by smart Linux users. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:. Executing the Bash Script Step 4:.
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. -turns off a permission. Chmodto turn the permissions on or off.
The chmod command can also be used to control the access permissions for directories. Let’s remember the access permissions of document.docx:. We can use the -l (long format) option to have ls list the file permissions.
The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo. As you know the file system of linux has a file access and control mechanism which determines how and who can access a file stored in a linux system.
To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all). To remove all existing permissions, set read and write access for the user while allowing read access for all other users, type:. Using chmod with Absolute Permissions.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files. (G)roup can read, can't write and can't execute.
How to Use the chmod Command on Linux chmod Modifies File Permissions. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Absolute Mode – Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions).
The third number specifies permissions for the owner's user group;. Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. R - Allows the contents of the directory to be listed if the x attribute is also set.;.
For example, you could set the metadata to display that you have write permissions to a file using chmod 777, but if you tried to access that file you would still not be able to write to it. The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file. The fourth number specifies permissions for everybody else;.
Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. The group ID of the file does not match the group ID or supplementary group IDs of the calling process.
Possible values (to set multiple permissions, add up the following numbers):. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory.
Again, we can use the octal notation to set permissions, but the meaning of the r, w, and x attributes is different:. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod. Group permissio view the full answer.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. To change the permissions of a file, one uses the chmod command, with the following syntax:. The command takes the general form:.
-rw-rw-r– We can set these same permissions with the symbolic notation:. The request is filtered by the umask. (Modes determine who can read, write, or search a directory or file.) Users with read access to SUPERUSER.FILESYS.CHANGEPERMS (a UNIXPRIV class profile), can use the chmod command to change the permission bits of any file.
The operator determines whether to add (+), remove (-) or explicitly set (=) the particular permissions. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. The calling process does not have appropriate privileges, that is, superuser authority (UID=0).
With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros. In Linux, we have 3 types of file permissions:. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set.
To better understand how the chmod command works, it’s prudent that we study the Linux file permissions model. These permissions determine which users can read, write or execute the files. Chmod changes the access permissions, or modes, of the specified file or directory.
How to Make Bash Script Executable Using Chmod Step 1:. But if you want to add this user to the group associated with "myfolder", you can run. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).
The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. For example, let's say you've downloaded a piece of software you want to share with other people on your system. The permissions are as follows:.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. The chmod command can accept numeric integers, such as 0664, which relate to user permissions.
To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. File Permissions in Linux using Chmod. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of. Viewing and Understanding File Permissions.
To restore Chmod execute permission with busybox, run:. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. The symbolic method and the absolute form.
Just in case Perl is available on your system, you can fix Chmod's execute permissions with command:. Chmod options permissions file name If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux.
# busybox chmod +x /usr/bin/chmod Method 7 - Using Perl. Select the permissions you require below. 1 = execute permissions;.
Chmod command is used to set file permission in linux/unix system. Chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can't execute. $ chmod 0 sample.txt Write by anyone $ chmod 002 sample.txt Execute by owner only $ chmod 100 sample.txt Execute by group only $ chmod 010 sample.txt Execute by anyone $ chmod 001 sample.txt Allow read permission to owner and group and anyone.
Use the chmod command to set file permissions. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:. In symbolic notation, we provide chmod with a comma-separated string using references for user (u), group (g) and others (o).
Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples.
$ chmod 777 sample.txt. Chown -R 755. Symbolic Mode The format of a symbolic mode is a combination of the letters +-= rwxXstugoa Multiple symbolic operations can be given, separated by commas.
Chmod is used to modify the permissions of a directory or file. Chmod octal value file-name. Creating a Bash File Step 2:.
The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument.

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Chmod Unix Permissions Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Softaox

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
Video Linux File Permissions Chmod And Chown Linux Org

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions

What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
%20access%20permission%20%EC%98%88)%20chmod%20644%20test.jpg)
Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
What Is Chmod 777

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Give Permissions In Ubuntu Itechzo Give Permissions In Ubuntu

Chmod Permissions Yaman S Website

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
1

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

What Are User And Group Permissions 荷树栋 开发者的网上家园

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Kirelos Blog

Chmod Calculator Takes The Hassle Out Of Directory Permissions Techfruit

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
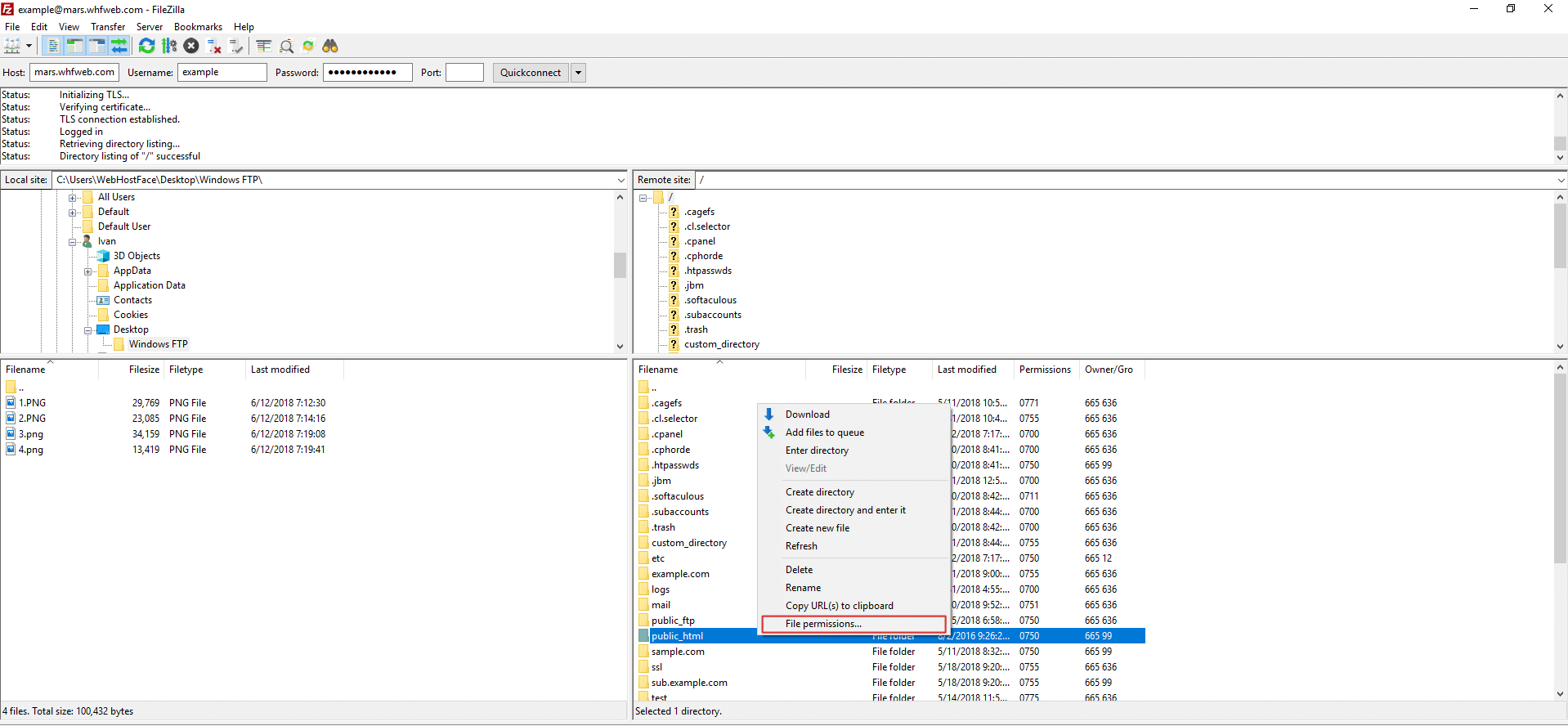
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Set File And Directory Permissions Using Chmod
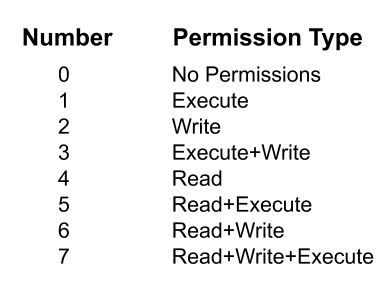
Understanding Permissions Jetapps
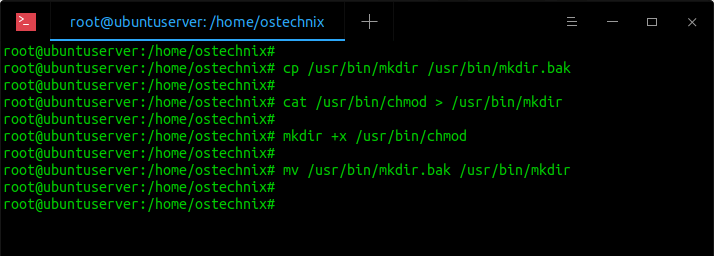
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Requisite Access Rights At Server
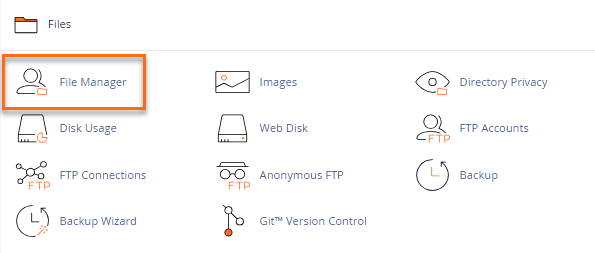
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium
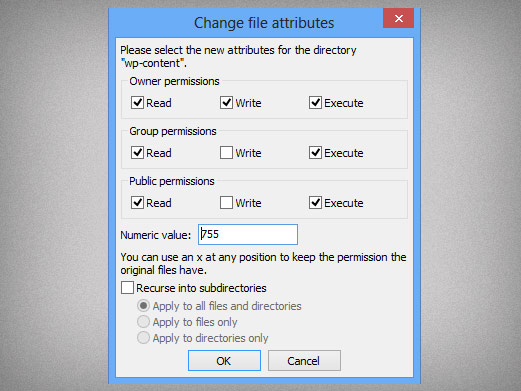
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

Ownership And Permissions
Change File Permissions With Chmod Github

Ownership And Permissions

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Chmod Command Calculator Easiest Way To Generate File Or Directory Permissions Product Hunt

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

Recommended File Permissions For Wordpress Asdqwe Dev

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Q Tbn 3aand9gcrojuqi6hxqmllhpyprxttzqvcdgkrg Jrkia Usqp Cau
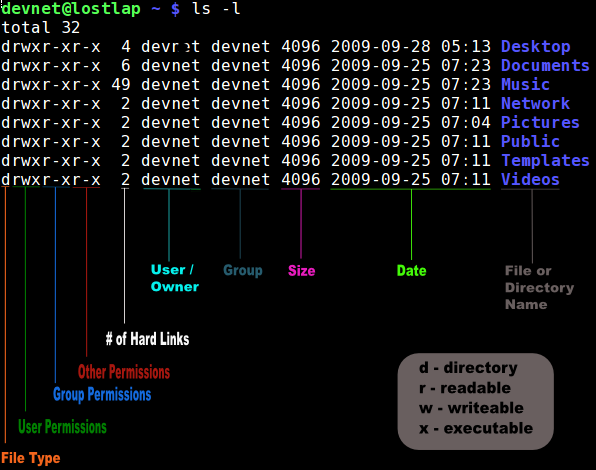
Chmod Archives Yet Another Linux Blog

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu
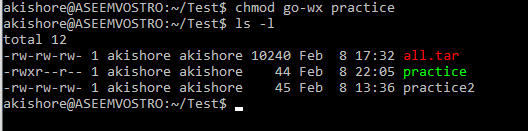
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Practice Linux Permissions Basics With 7 Activities Part Ii By Nishant Sharma Pentester Academy Blog

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Give Write Access Chmod Unix

14 Permission And Modification Times

Understanding File Permissions

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Permission And Chmod Ppt Download

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux Change File Permissions Three Commands Chgrp Chown Chmod Programmer Sought

Unix Permissions

More About Linux File Permissions

Give Write Access Chmod 644
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
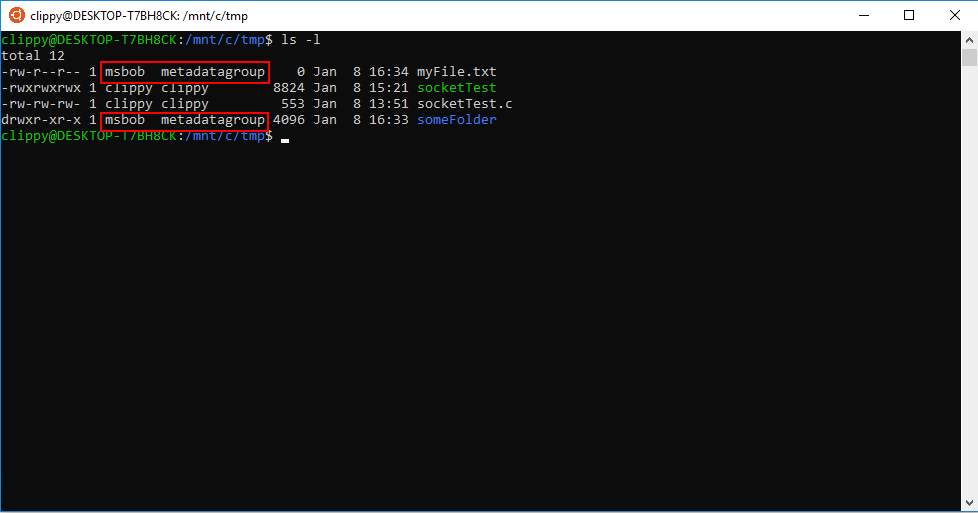
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
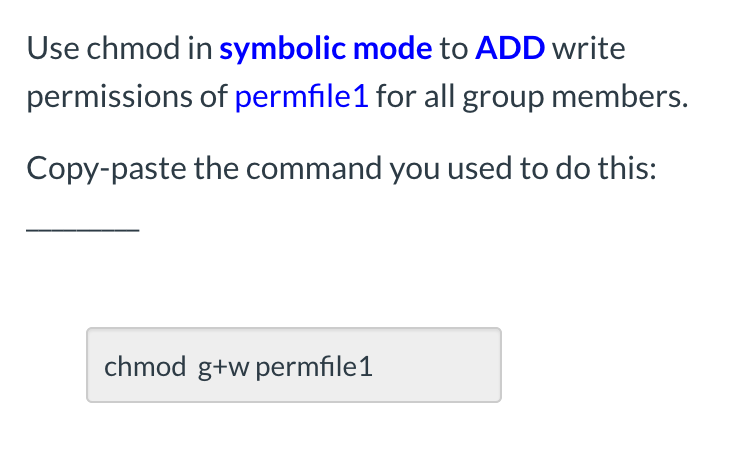
Solved Use Chmod In Symbolic Mode To Add Write Permission Chegg Com



