Chmod Command In Linux Recursively
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
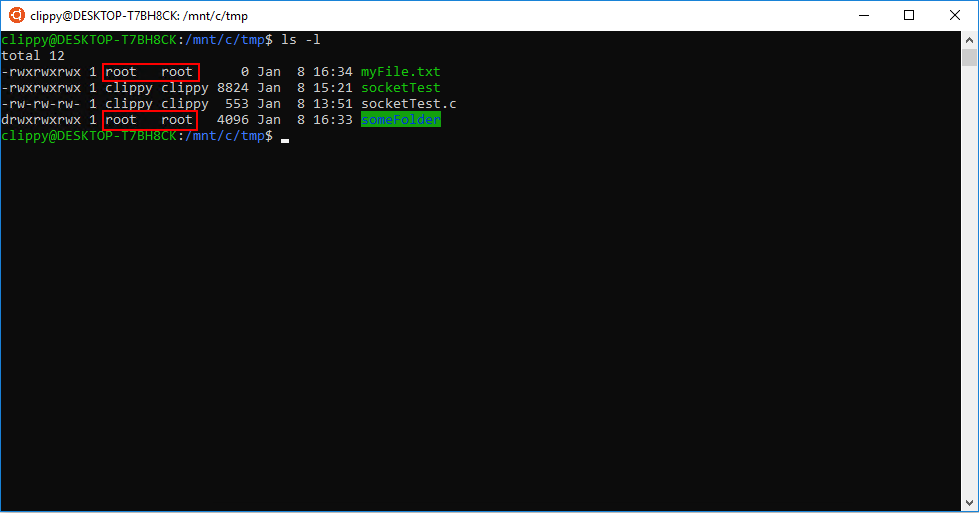
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
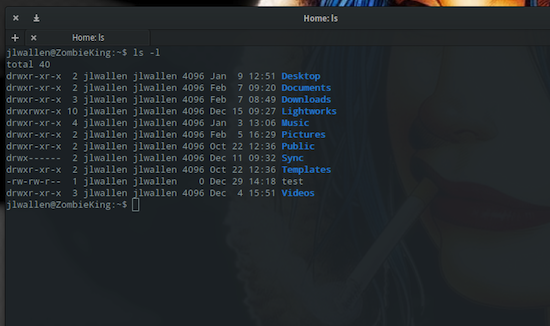
Getting To Know Linux File Permissions Linux Com
How to Recursively Change the File's Permissions in Linux Chmod Recursive #.

Chmod command in linux recursively. Changing the permissions recursively using -R. Like many other Linux commands, chmod has a recursive argument, -R, which allows you to operate on a directory and its contents recursively. Suppose that user `joe' wants to copy the file `prog.f' from user `fred.' At the Unix prompt, Fred should type.
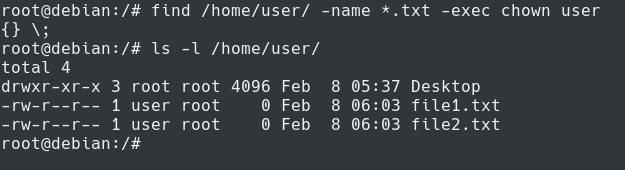
Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:. Find /directory/of/interest/ -type f -iname "*.sh" -exec chmod +x {} \;. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. Chmod — Change the permissions of files or directories. Chmod command has an option --preserve-root to prevent chmod from acting recursively on /.
In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions. 3) close, open nautilus, right click on folder or file, select permissions and enjoy…. Chmod permission file chmod permission dir chmod User AccessRights Permission file We use the following letters for user:.
Chmod option mode files Options. Output a diagnostic for every file processed -c :. As Linux administrator, we always use chmod command to change file permissions in Linux.
How to do it in one line using find and excluding the directories. Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux’s chmod command. 4+2+1=7 $ chmod 777 sample.sh.
40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Chmod 700 -R directory.
Chgrp -hR staff /office/files. Sample Shell Script To Change Permission Recursively. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute.
Normal files only (skip directories, symlinks, named pipes and sockets, and the special files found in /dev). The easiest way to use the chown recursive command is to execute “chown” with the “-R” option for recursive and specify the new owner and the folders that you want to change. In this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command.
To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode"). Chmod 4777 Chmod 4777 (chmod a+rwx,ug+s,+t,g-s,-t) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. The chmod command changes the access mode of one file or multiple files.
This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work. Chmod permissions file OR:. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
Change the owning group of /office/files, and all subdirectories, to the group staff. You may have noticed that if you apply permissions through the above chmod command, these permissions are only applied to the file or directory specified in the command. In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals.
1) open gconf (for example in terminal or Alt+F2) 2) in gconf-editor under /apps/nautilus/preferences select “show_advanced_permissions”. A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Give read, write and execute permissions to everyone. Chmod g-x file1 :. Linux - Newbie This Linux forum is for members that are new to Linux.
-R – Recursively change ownership of directories and their contents. To make this possible you can use the find command and search for all files with a .sh extension and then run the chmod command on each one found:. If you specify the -h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change.
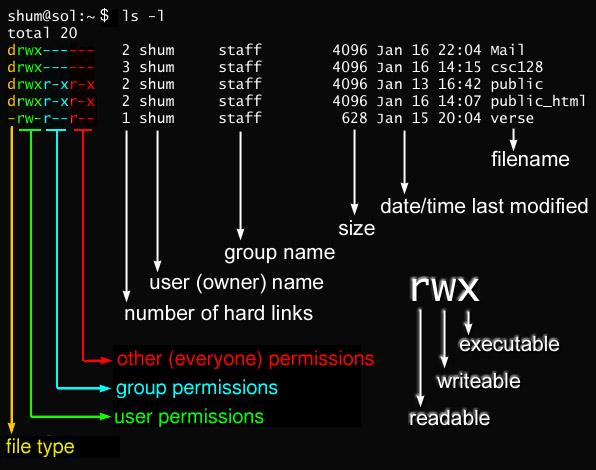
Both chmod and chown can be run recursively on directories, to change file permissions for everything within those directories. If it’s in the same directory, you may need to use chmod command with file name and new file permission to be applied. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
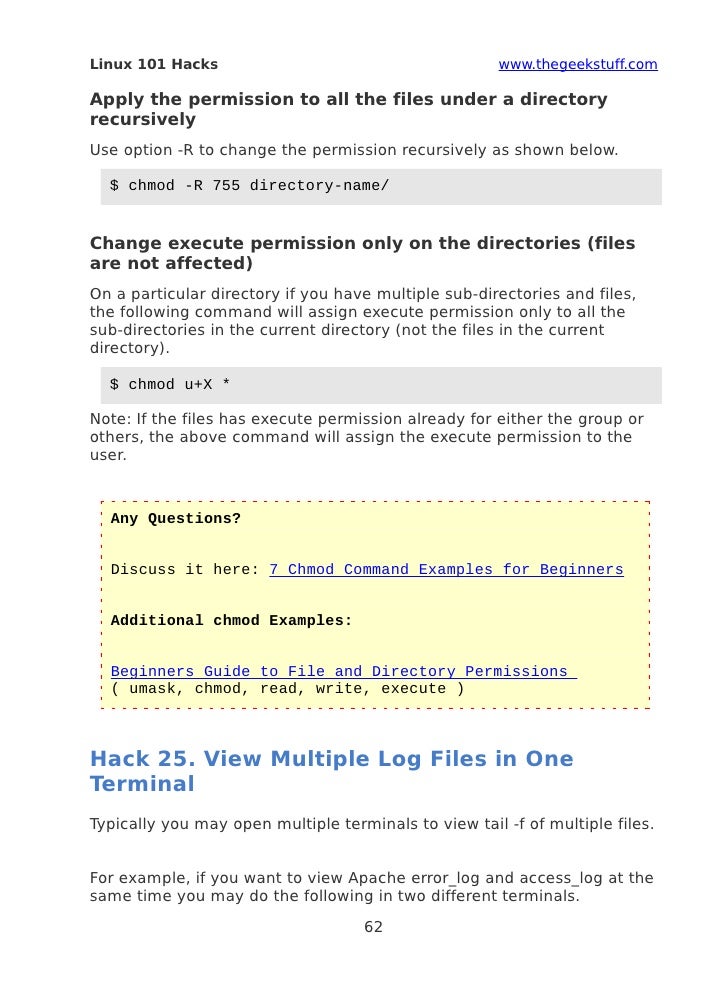
This tutorial explains CHMOD and CHOWN commands that are broadly used in Linux. In this tutorial, we will show you how to change file permissions recursively with chmod and find command in Linux. $ chmod -R 755 directory-name/ 7.
It means revoking execute permission from file group. The syntax for the chmod command is:. The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system.
How to use chmod?. The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. Sudo chown 1001:1001 at.c.
These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. In the example below the executable flag is cleared and then set for all directories recursively:. You can use chmod with the X mode letter (the capital X) to set the executable flag only for directories.
(O)thers can read, can write and can execute. Chmod command in Linux -v :. The first step is to create a new text file with .sh extension using the following command.
You can change file permissions in this format:. Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners. It will not be applied to the sub-directories or files within a directory.
Creating a Bash File. Meaning of recursive in chmod command User Name:. If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod --version command as shown below.
Change execute permission only on the directories (files are not affected). Change the owning group of the file file.txt to the group named hope. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD. The chmod command changes the access mode of one file or multiple. Chmod go+x ~ This command changes the mode of Fred's home directory (represented by the ~), giving permission to all users to get to files in that directory.
For example, this command will find. Chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that. To recursively set permissions of recordsdata based mostly on their sort, use chmod together with the discover command.
If it is not in the man pages or the how-to's this is the place!. Setuid and Setgid Bits chmod clears the set-group-ID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges. Use the chown and chmod commands to secure file access on your system.
Like verbose but report only when a change is made –reference= FILE :. CHMOD and CHOWN. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command.
The overall syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. Basic Syntax of CHMOD Recursive The basic syntax of the chmod command is shown below:. The chmod command with the -R choices means that you can recursively change the file’s permissions.
Which method is better, find -exec or xargs?. Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. Root@node051 ~# chown -c --preserve-root tom / changed ownership of '/' from root to tom.
Id — Display real and effective user and. I used to work with linux command in the University and after a pause of few years… it brought me back to ‘beginers mode’ when I needed to use chmod. In general, the files and directories should not have the same permissions.
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory.The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory. This option should be used with -R option to take effect. You can either use symbolic representation of changes or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed). After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands. Find All Directory or File (Recursively) Only And Execute Command (Chmod) December 14, 17.
By recursive, It is meant that the command will attempt to operate on all objects below the specified directory rather than just the directory itself. In this tutorial, we look at the chmod. To recursively function on all recordsdata and directories below a given listing, use the chmod command with the -R, (–recursive) choice.
How to check chmod command version. One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. The chown command stands for “change owner” is used to change the owner.
Chmod Recursive # The chmod command means that you can change the permissions of recordsdata utilizing symbolic or numeric mode. -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems.
Find ./mydir -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. Read, write and execute:. You can also use chmod as the -exec option for find, which lets you change file permissions throughout the system.
Recursively change the permissions of a directory. The syntax of chmod command is chmod options mode filename THe important options are:. The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering.
$ chown -R <owner> <folder_1> <folder_2>. Possession is Nine-Tenths of the Law. -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;.
We hope the How to Recursively Change the File’s Permissions in Linux help you. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it. Use option -R to change the permission recursively as shown below.
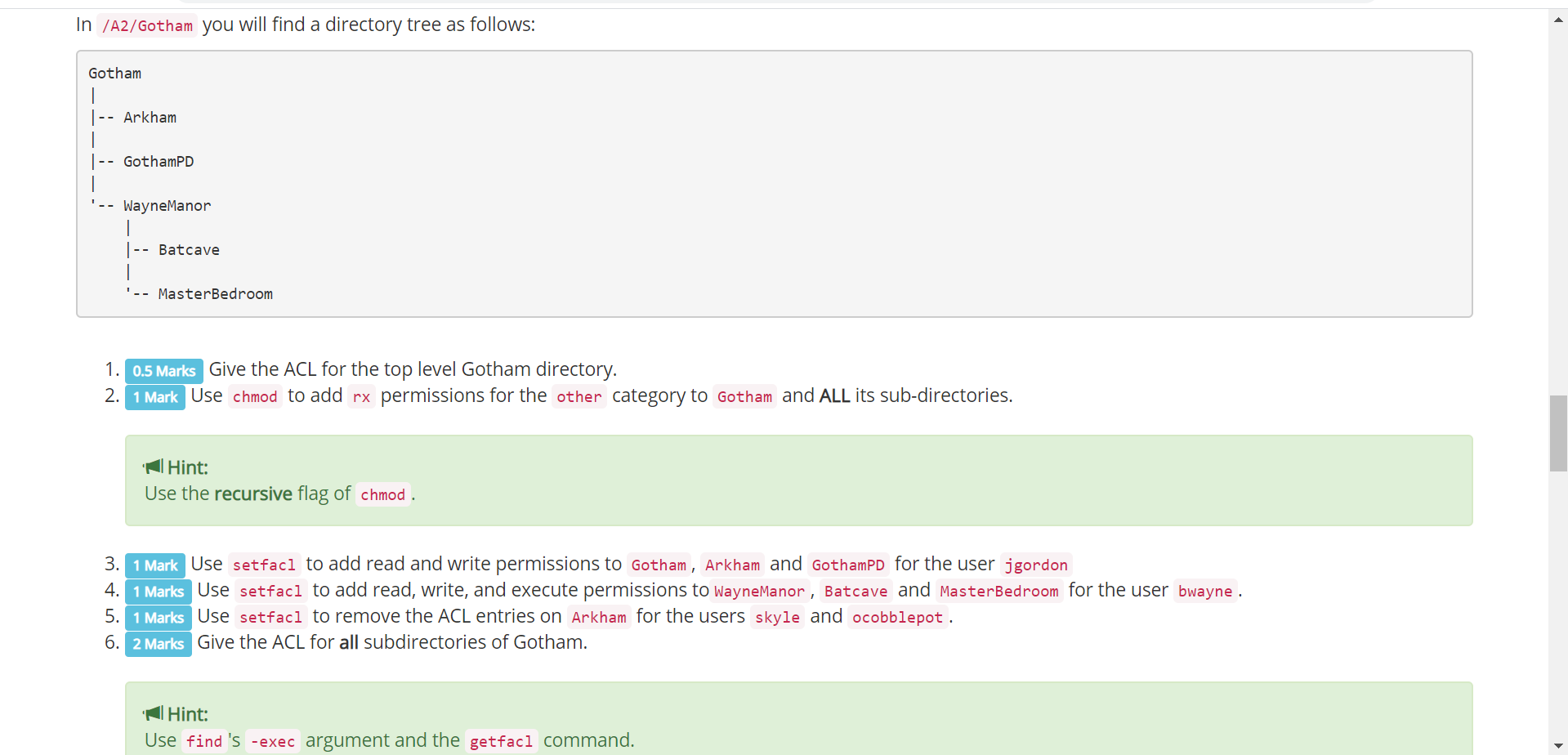
The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder.
Descend directory arguments recursively while setting modes.-f:. Verbose Chmod Examples in Linux / Unix:. We can set or remove (user access rights) file permission using the.
If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command. Chown — Change the ownership of files or directories.
Most files do. Examples of chmod command /chmod recursive. A command line / terminal window ( Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Alt+F2) A user account with sudo privileges (optional) A Linux system.
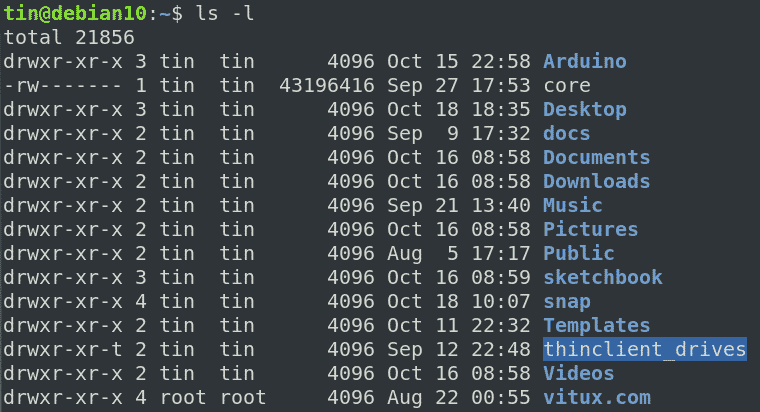
Just starting out and have a question?. I was trying to chmod folders and files with:. As you can see from below output current chmod version is 8.22.
Chmod is a GNU utility which is provided as part of coreutils rpm in Linux distributions chmod is short abbreviation for " Change Mode " It is used to change the file mode bits of each given file/directory according to mode. Use FILE’s mode instead of MODE values – R :. To do this, use the uppercase -R flag:.
Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command. Using the find Command #. Linux · Unix · Ubuntu;.
Chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file. It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. But in Linux, ownership is a massive part of file security, with file permissions providing the remainder of it. There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux.
As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility. It could be a single file or multiple files. It means giving read/write/execute permission to file owner but revoke every permission from group and everybody else.
If you specify both the -h flag and the -R flag, the chmod command descends the specified directories recursively, and when a symbolic link is encountered, the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link is not changed. Or so they say. Examples chgrp hope file.txt.
It may happens many times in a day, it depends on your environment size and team size. But I was wondering:. Linux ubuntu Apply chmod 755 to directory and sub-directories only (excluding files).
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories. This command will set the user and the group ownership to mary. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.

Linux File Permission Explained In Easy Language
12 Frequently Used Hadoop Hdfs Commands With Examples Usage Dataflair
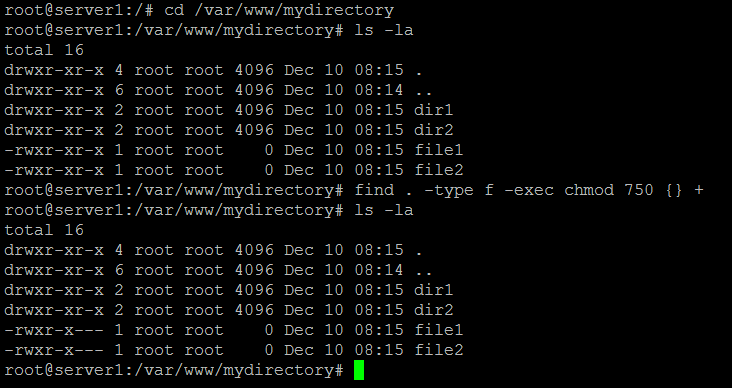
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Rm Unix Wikipedia

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Find Files With Matching String In Linux Grep L Command Example Java67

File Permissions Rhel 7 Tutorial
Linux Chmod

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Unix Commands Command Line Interface File System

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line
2

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab
New Bash Linux Cheat Sheet Wallpaper Download Free 40 X 3050px

A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More

Course 102 Lecture 14 Users And Permissions

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux Introduction Commands
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

Linux To Recurse Or Not Network World

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Read Write Access Chmod 775

Chmod Command Tutorial How To Recursively Set Permissions In Sub Folders

Learn How To Resetting File Permissions Ownership On Linux Systems Linux Learning System
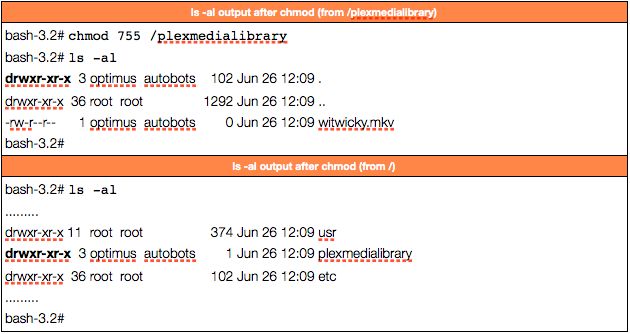
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

10 Ways To Use The Chown Command With Examples Foss Linux

Chmod Command Kali Linux Class 5 Youtube

Write A Unix Linux Find Like Command Myfind In Chegg Com
How To Create Write A Simple Sample Linux Shell Bash Script 5 Steps Instructables

Delete Remove A Directory Linux Command Nixcraft

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
What Is Chmod In Windows

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat
Linux Command Line Adventure Midnight Commander
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This
1

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
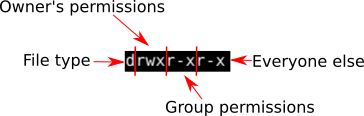
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
12 Frequently Used Hadoop Hdfs Commands With Examples Usage Dataflair

Chgrp Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Use All Linux S Search Commands

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux Chmod

Read Write Access Chmod 775
Linux Chmod Tips
Solved Please Provide Commands For These Steps To Be Done Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod Wikipedia

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux Permissions Deep Dive Part 1 By Runcy Oommen Medium
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint
Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example

How To Set A File To This Drwxrwsrwx Permission On Ubuntu Stack Overflow

Chmod 0400 Means

How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Tree Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

14 Permission And Modification Times

Command Line Quick Tips More About Permissions Fedora Magazine

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
10 Rm Command Examples For Linux Beginners
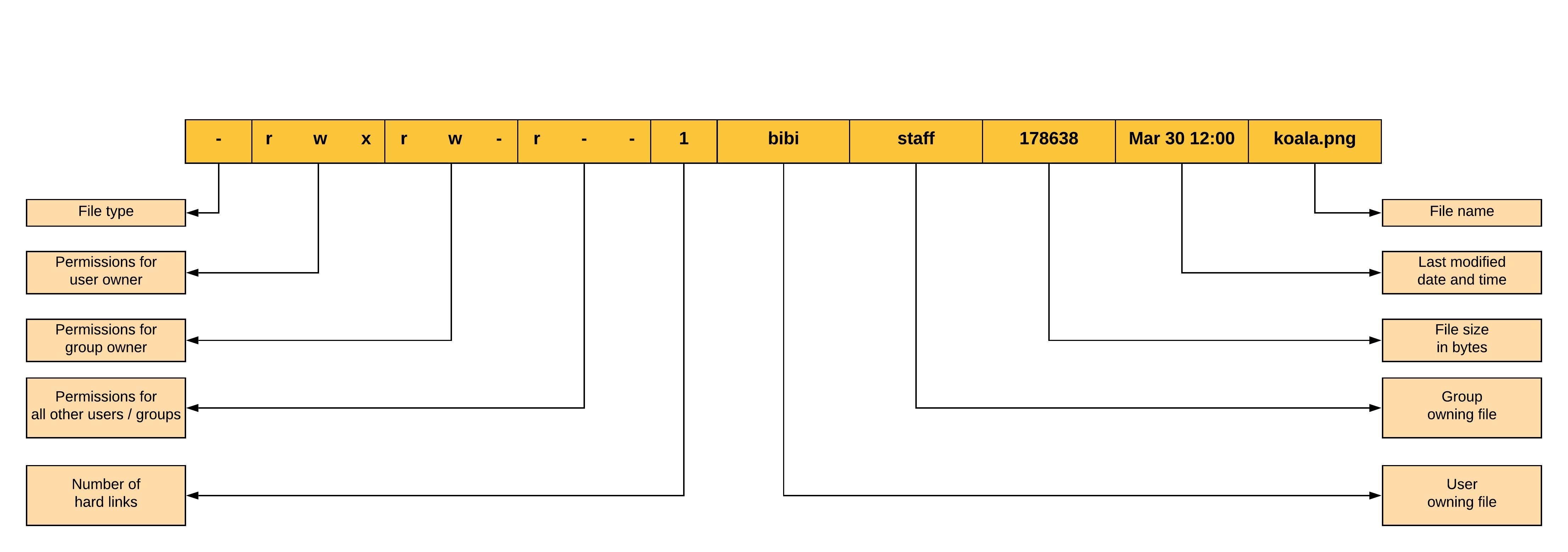
Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding
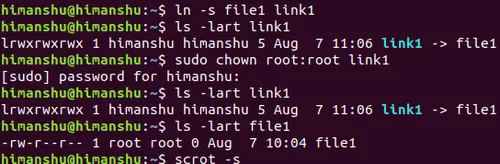
Linux Chown Command Tutorial For Beginners 12 Examples



