Chmod Octal Mode

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth
Chmod Help

Linux File Permissions With Examples Welcome To Mariobytes Media

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator By Chmodcalcu Issuu

What Is Ftp Chmod Chmod Change Mode Impress Org

How To Get Octal File Permissions On Linux Unix Command Line Nixcraft
The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and restricted deletion or sticky (1) attributes.

Chmod octal mode. Using octal syntax for chmod allows setting the absolute permissions for owner, group, and other in one quick command. One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats.
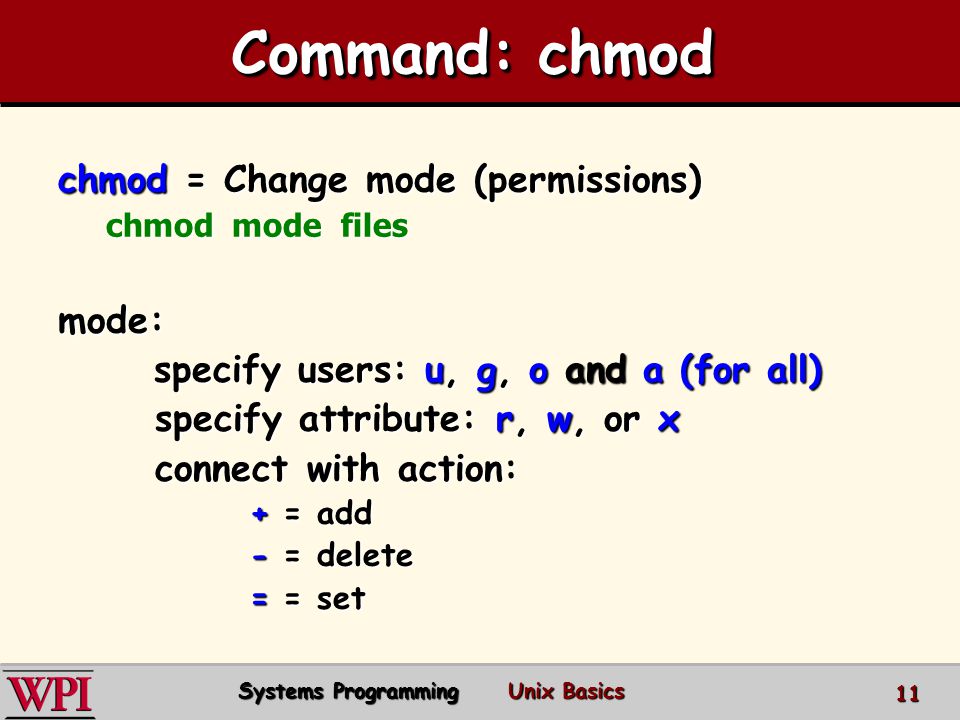
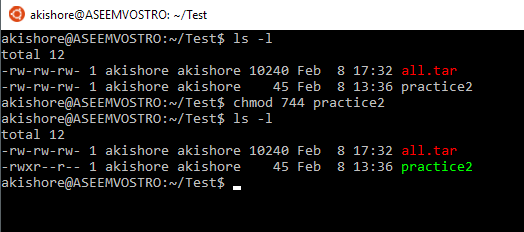
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. How to use chmod?. A superuser or the file owner can use a chmod command or chmod() function to change two options for an executable file.
It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. The command takes the general form:. Alternatively, you can utilize the symbolic mode (using alphanumerical characters) and use the command:.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. You can change file permissions in this format:.
The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. In the next example we will change file.txt's permissions to rwxr-xr-- with a following symbolic specification:.
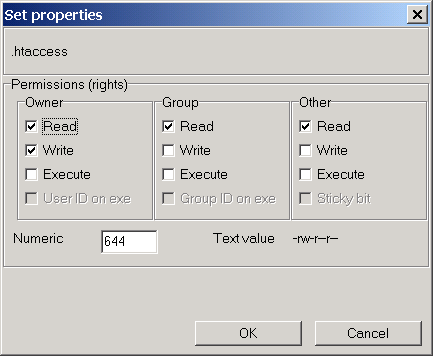
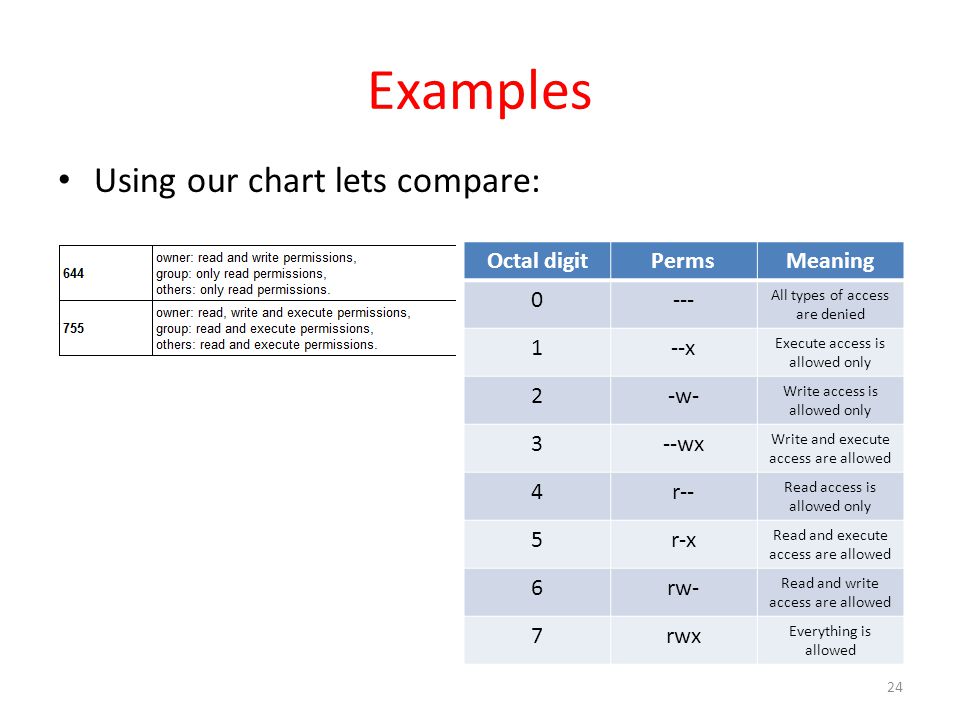
Chmod Permissions for chmod 644. The mode can be defined symbolically or numerically (absolute mode). These octal values, can be used to change or manage a file or directory's permissions, using a well known command-line-utility called chmod.
Chmod changes the access permissions or modes of the specified files or directories. 0644 is okay, but "0644" is not. Instead of “u=rwx,go=rx”, you would have “755”.
The mode '0775' would mean:. Symbolic specification is just another way to change file and directory permissions. When symbolic links are encountered, their mode is not changed and they are not traversed.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. Thus the sprintf must use the %o formatting character, so that the passed integer value is really represented as an octal number to the CHMOD site command for the FTP server.
There are two ways to represent the MODE:. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. The options are set in two file mode bits:.
$ chmod 764 file.txt. You can specify the mode value on the command line in either symbolic form or as an octal value. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod.
$ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. We only use commas to separate them.
The mode option can be either a symbolic_mode expression or a nonnegative octal integer. The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. Chmod (change mode) on Unix-ohjelma, jolla muutetaan tiedostojen ja hakemistojen käyttöoikeuksia.Käyttöoikeuksia kutsutaan Unixissa yleisesti myös moodeiksi (mode).
You can either use symbolic representation of changes or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Group can read, write and execute. Chmod -R a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx folder_name.
You either use a full three-digit octal number, or you don’t use octal with chmod at all. The chmod -R option allows you to recursively descend through directory arguments, setting the mode for each file as specified. Chmod +x filename.sh to make filename.sh executable.
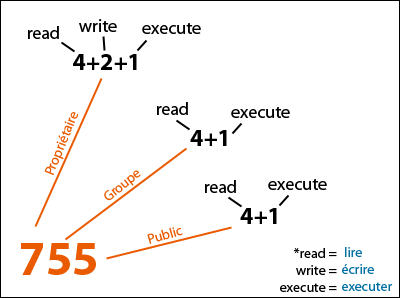
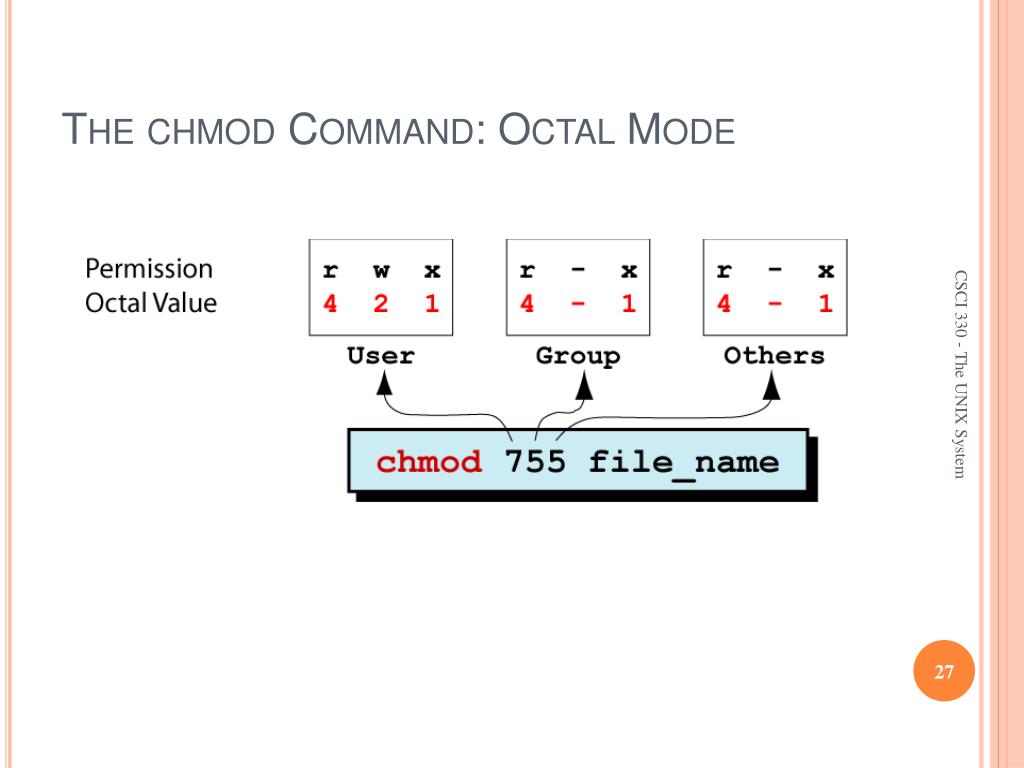
In the example above, the permission is defined using the octal/numerical mode (755). A symbolic mode has the form who op permission op. Chmod +x new_script.sh Setting Permissions for Multiple Files.
Specifies the octal values that represent the permissions for the file owner, file group, and others, in that order. Let's see how we can change file.txt permissions to rwxr-xr-- with octal mode:. The first element of the list must be the numeric mode, which should probably be an octal number, and which definitely should not be a string of octal digits:.
To convert it to string i use:. Umask is a 3 digit octal number. $ chmod nnn filename:.
The first digit is optional and used to define special flags while the second to fourth are used to set permissions for the file’s owner, the user group, and other users outside that group. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Obtaining a specified "Octal Value" usually starts with a file's "Symbolic Value", and transmuting it to it's corresponding number value.
Modes determine who can read, change or execute a file. Chmod -R 644 folder_name. We can apply permissions to multiple files all at once.
Ugoa +-= perms. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. To change a file's permission mode bits, the user of chmod must be either the owner of the file or the superuser, root.
Owner can read, write and execute;. As we discussed above we can change permission using Numerical and Alphabetical way, here I have explained both methods with all tricks. Here’s a chmod example using for setting permissions so that:.
Oikeuksien muuttamiseen chmodissa voidaan käyttää joko numeerisia tai symbolisia moodeja. And to retrieve it i use atoi, but it does not seem to work. Chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r test.txt Note:.
The format of a symbolic mode is:. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g.
You can do the same in symbolic mode. Change mode (chmod) is a Unix operating system command used by administrators and programmers to set or change the access permissions of a file or directory. The op part of a symbolic mode is an operator.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify. These settings determine the level of access to be granted to the given file or directory. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others.
Read (or set user-ID) 2:. Another way to specify permission is by using the octal/numeric format. See also oct if all you have is a string.
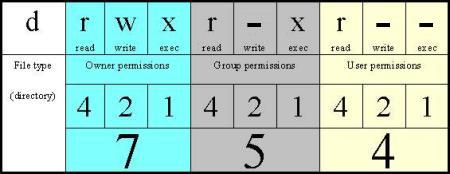
Sprintf (mode, "%o", statr.st_mode);. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1). A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1.
Let’s say we want to remove the write permissions for the “other” users from files that have a “.page” extension. Owner can read, write and execute;. Chmod.(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files.
Numeric/octal mode To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. Using octal values to change access You can also use numbers (octal values) instead of letters to set the permissions. Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmod command to change file permissions on a file or directory.
How to set permissions with chmod in octal mode. There are four digits in the command;. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE….
To view these online, enter. Additionally server-side languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation. Using letters is easier to understand for most people.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you. Chmod is short abbreviation for "Change Mode" It is used to change the file mode bits of each given file/directory according to mode.
Write (or set group-ID) 1:. Changes the permissions of a list of files. These are the files in the current directory:.
The chmod command was first used in ATT Unix 1 and is still in use today by Unix-like operating. Set-user-ID (S_ISUID) with the setuid option. Set-group-ID (S_ISGID) with the setgid option.
The syntax requires three octal digits, each representing the owner, group, and other permissions, respectively. The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. With chmod, these modes are defined in an octal format, using 0 through 7.
Select the permissions you require below. OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command:. After changing a file's mode to 644 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as:.
Group can read, write and execute. There is no space between the categories;. Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file.
The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. Permissions masking with umask, chmod, 777 octal permissions Ian!.
When a symbolic link is encountered and you have not specified the -h flag, the chmod command changes the mode of the file or directory pointed to by the link and not the mode of the link itself. My problem is that i have to convert the octal value from st_mode to a string, store it in the archive file (the fourth tag in the header),then extract it and use it with the chmod syscall. Returns the number of files successfully changed.
There are no relative assignments of permissions using octal. The symbolic_mode has the following form:. Technical Description chmod changes the file mode of each specified FILE according to MODE, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
And there you have it:. Use the octal CHMOD Command:. In this case, ---x--x--x converted to it's Octal or Number value is.
Chmod examples using octal mode :. Omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. We can do this with the following command:.
The "mode" parameter of the PHP5 ftp_chmod function is an integer value that is supposed to be given as an octal number, like the argument for the "chmod" command line tool. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. If you specify the -h flag, the chmod command prevents this mode change.
Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify. There are only three bits in an octal mode:. Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories.
It takes the following syntax:. Change permissions in absolute mode by using the chmod command. Chmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (a+rwx) or with octal numbers (777).
Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission) Using numeric modes (An octal (base 8) number that represents the mode). # chmod LIST.

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Chmod Wikipedia
Chmod 0400 Means
Media Management Permissions Error Must Contain A Valid Unix Permissions Octal Issue 3869 Sonarr Sonarr Github

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

0x05 Slae Msfvenom Samples A Journey In Infosec
Media Management Permissions Error Must Contain A Valid Unix Permissions Octal Issue 3869 Sonarr Sonarr Github
Class File Tree Structure Home Csc156 Yourusername Chegg Com

Chmod 0400 Means

Module 4 File Security Security Overview File Ownership Access To Files And Dircetories Changing File And Directory Ownership Changing File And Directory Ppt Download

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire

Linux Mac And Unix File Permissions Part 1 Steven Barrett Co Uk
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Csci 330 The Unix System Unit V Permissions All Access To Directories And Files Is Controlled Unix Uses Discretionary Access Control Dac Model Each Ppt Download

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Chmod File Permission And The Octal Notation Netseed

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How To Get Octal File Permissions From Command Line In Mac Os Osxdaily

What Are User And Group Permissions 荷树栋 开发者的网上家园

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Csci 330 The Unix System Unit V Permissions All Access To Directories And Files Is Controlled Unix Uses Discretionary Access Control Dac Model Each Ppt Download

How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

Chmod Linuxconfig Org
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau
Linux Chmod Tips
Linux And Unix Chmod Command Knowledge Hub

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

File Permissions Mode 0777 Vs 777 Digital Fortress
Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Unix Permissions
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Csci 330 The Unix System Unit V Permissions All Access To Directories And Files Is Controlled Unix Uses Discretionary Access Control Dac Model Each Ppt Download

Unix File Permissions Computer Science
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 0400 Means

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod Chown Not Working Solved V3 Testing Sonarr Forums

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Linux Chmod Calculator Chmodcalculator

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Common Bash Commands

06 Users Groups And Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Chmod 0400 Means

Chmod 0400 Means

File Permissions How To Use Chmod Command Youtube

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
Ppt Csci 330 The Unix System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod Man Page Man Lit Le Manuel

14 Permission And Modification Times
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Class File Tree Structure Home Csc156 Yourusername Chegg Com

Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Using Chmod Command Octal Youtube

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
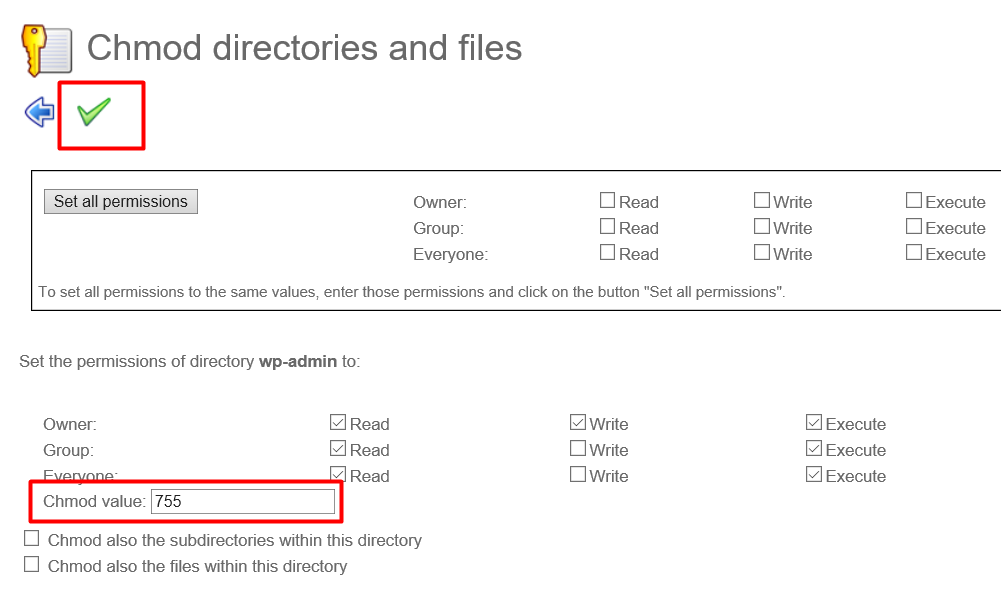
Chmod 0400 Means

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
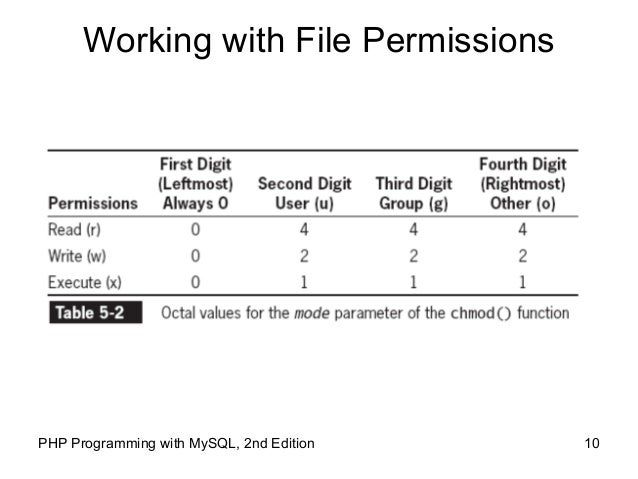
A Quick Introduction To Unix Permissions Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
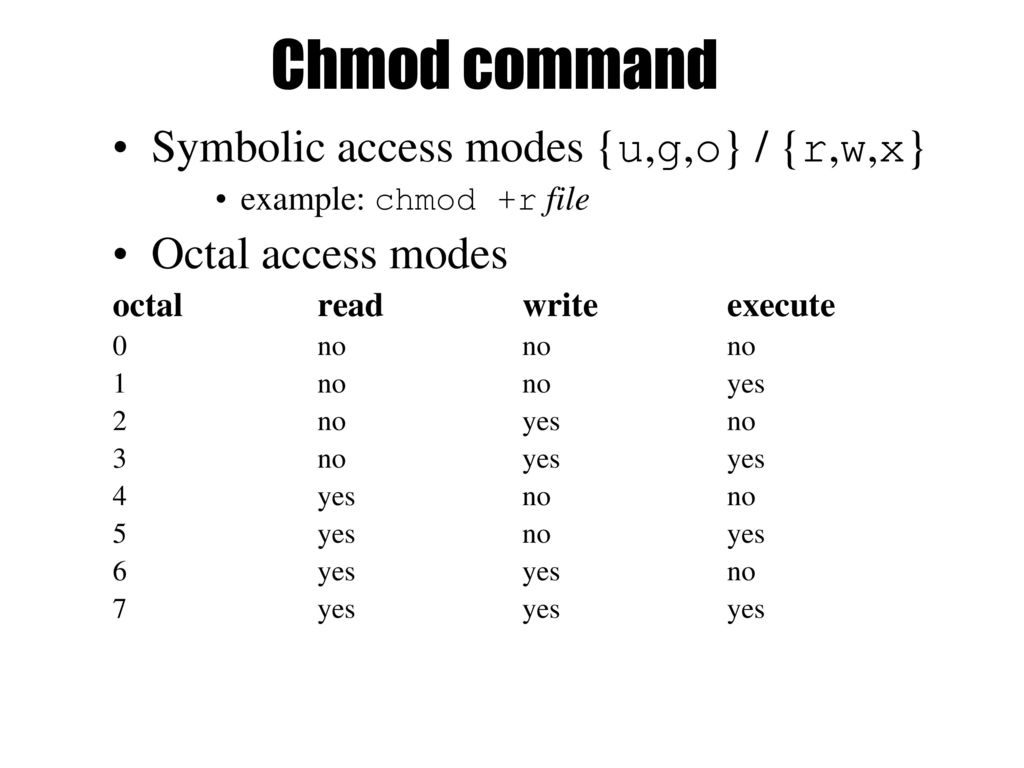
Chmod 0400 Means

Umask Wikipedia

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs

Chmod 0400 Means
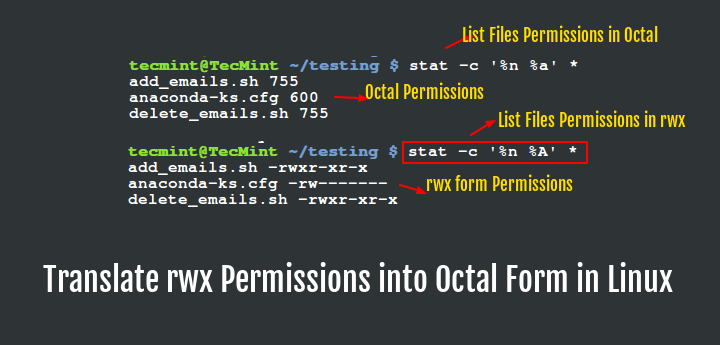
Translate Rwx Permissions Into Octal Format In Linux

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Solved Chmod Can Be Used To Change The Mode Of The File Chegg Com

Changing Permissions In Linux System Dev

Managing Linux Permissions

File Security And Access Control Ppt Download

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Read Write Access Chmod 775
A0s6e Hzewyrim
Q Tbn 3aand9gct7wt7gzhduflbfyn8phh8frjezj69hwxbeqqg4p T9 V8epo92 Usqp Cau

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

What Is Umask And How To Use It Effectively Liquid Web
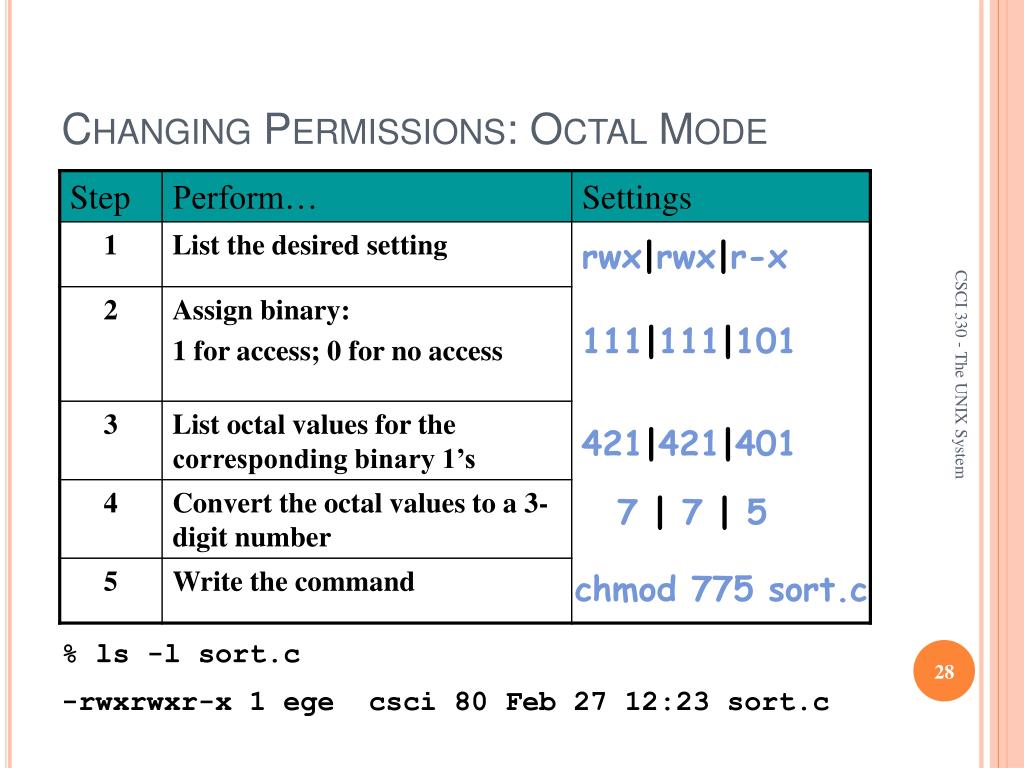
Ppt Csci 330 The Unix System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

File Security Viewing Permissions Ls L Permission Values Ppt Download



