Linux File Permissions Chmod Example

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Unix Permissions

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
Chmod is how we handle the file permissions.

Linux file permissions chmod example. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. Let’s check the new permission on this file:. File Permissions in Linux/Unix with Example Ownership of Linux files.
With this next one, owner will have read and write while group and everyone else have read permission. To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. The linux command chmod can be used to change the permission of a file or directory.
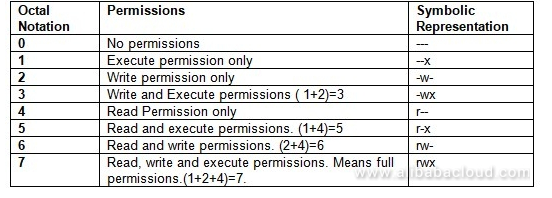
Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. Owner can read and write, nothing else for anyone. Chmod octal value file-name.
It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. 6 = rw-7 = rwx For example:. First is Symbolic Notation and second is octal notation.
Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission). In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. As explained in the article Permissions in Linux, Linux uses a combination of bits to store the permissions of a file.We can change the permissions using the chmod command, which essentially changes the ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’ characters associated with the file.
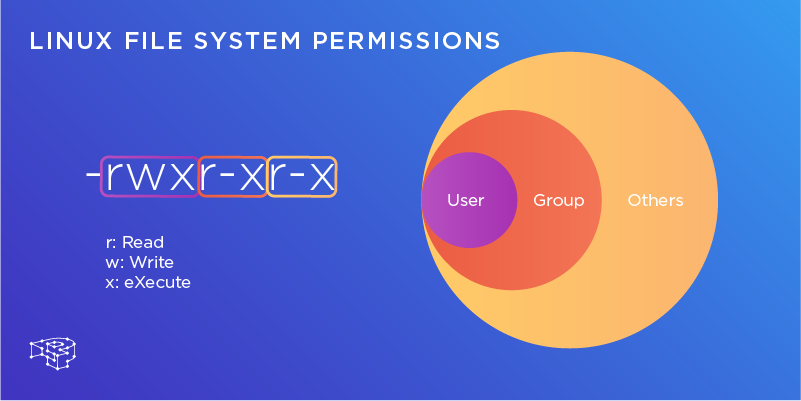
There are two ways to represent the MODE:. Linux File Permissions Explianed, let's understand linux files and permissions in a simplified manner, let's play with Linux File permission. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others.
With this next one, owner will have read and write while group and everyone else will have no permissions whatsoever. $ find /home/user/demo -type f -print. Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories.
The existing permissions have been removed, and the new permissions have been set, as we expected. Chmod command is used in two ways :. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
What is chmod ?. Txt pattern with chmod command. How to use chmod?.
Setting Permissions for Multiple Files. And it also allows to change and modify the permissions to a set of people as per the requirements. The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation.
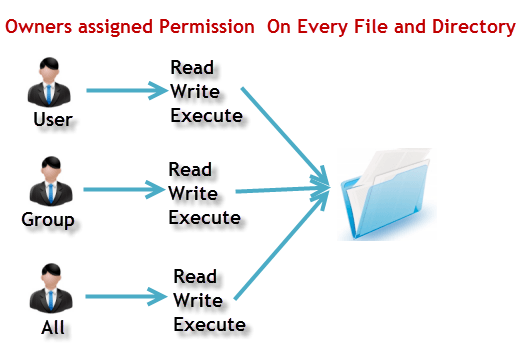
Further, the ownership of files also depends on the uid (user ID) and the gid (group ID) of the creator, as discussed in this. Following are some examples:. Every file and directory on your Unix/Linux system is assigned 3 types of owner, given below.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. Here roles are User.
Or similarly, we can take away write access for the group by calling:. Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others. To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal.
Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. For mode detail on chmod concept command, you can read this article for newbies and advanced Linux users. Below is the command's general structure:.
To change the file permission of multiple files, specify the file pattern with the chmod command. So I already own those files and folders, without having to change anything. The chmod() function shall change S_ISUID, S_ISGID, S_ISVTX, and the file permission bits of the file named by the pathname pointed to by the path argument to the corresponding bits in the mode argument.
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute and. # alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes.
Chmod is Linux command used to change file permissions.chmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permission.chmod 755 is popular use case for chmod .chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications. Conclusion # You successfully learned how to use chmod command to set or change the file and directories permissions using either the symbolic or numeric mode. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:.
Lets see few example. Both forms can be interchangeably used. Chmod 327 foldername will give write and execute (3) permission for the user, w (2) for the group, and read, write, and.
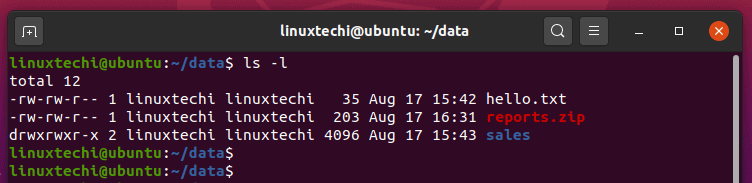
The output lists the permissions of all the files in the directory. In this article, I will take you through 11 Popular Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma).
0 = ---1 = --x;. To make this modification you would invoke the command:. Following is a sample of ls -l command output.
Linux as a multi-operating system sets permissions and ownership to ensure security for a file and directories of the users. So for an example, lets say I have a file named file1 that currently has the permissions set to _rw_rw_rw, which means that the owner, group and all users have read and write permission. Chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux.
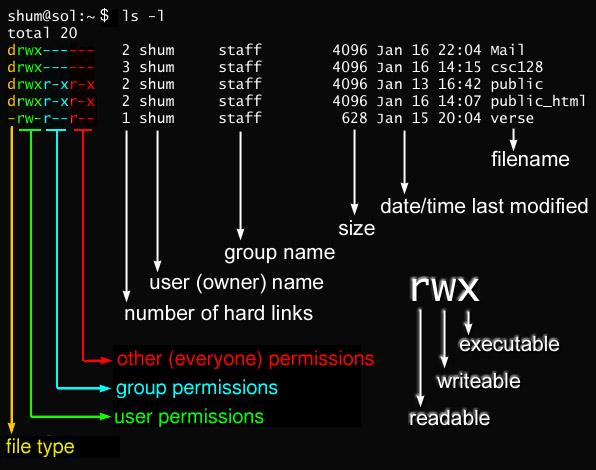
Just for the reminder, the following symbols are used for file permissions. Add the file’s owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file’s group have:. In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls -l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format.
Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory. Chmod 777 foldername will give read, write, and execute permissions for everyone.;. Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners.
For example, to change the permissions of all files and subdirectories under the /var/www/html directory to 755 you would use:. Chmod 600 /path/to/file chmod command examples in symbolic mode. Make permission for a file same as another file (using reference) If you want to change a file permission same as another file, use the reference option as shown below.
To apply the setuid bit to a file, we would have run:. This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. $ ls -l sample.sh -rwx-rw-r-- 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 03:12 sample.sh Here in the above example:.
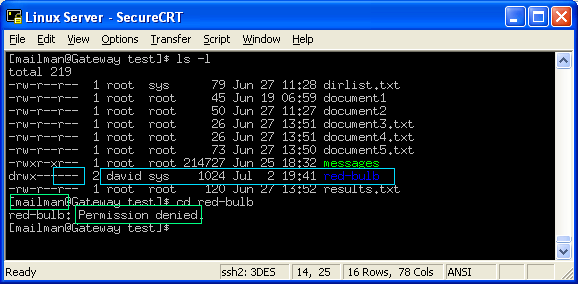
$ chmod o+t test The use of special permissions can be very useful in some situations, but if not used correctly the can introduce serious vulnerabilities, so think twice before using them. To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls -l command as shown below:. -rw-r--r-- 1 john john 272 Mar 17 08:22 test.txt.
Both are described below:. Change file permissions in Linux. Chmod 644 /path/to/file chmod 600:.
Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. Symbolic chmod permission examples. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755.
The application shall ensure that the effective user ID of the process matches the owner of the file or the process has appropriate privileges in order to do this. This is illustrated in the calculation below. Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu.
For example, we can add write permissions for others:. To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command :.
Give read, write and execute permission to the file’s owner, read permissions to the file’s group and no permissions to all other users:. 2 = -w-3 = -wx;. Use matt has the read, write and execute permissions on the file.
755 can be separated as. We can set these same permissions with the symbolic notation:. Chmod 700 foldername will give read, write, and execute permissions for the user only.;.
In this article, we have learned the Linux file permissions, commands, and some examples in brief. It allows the permissions to be changed in either Symbolic form or in numerical form. For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6.
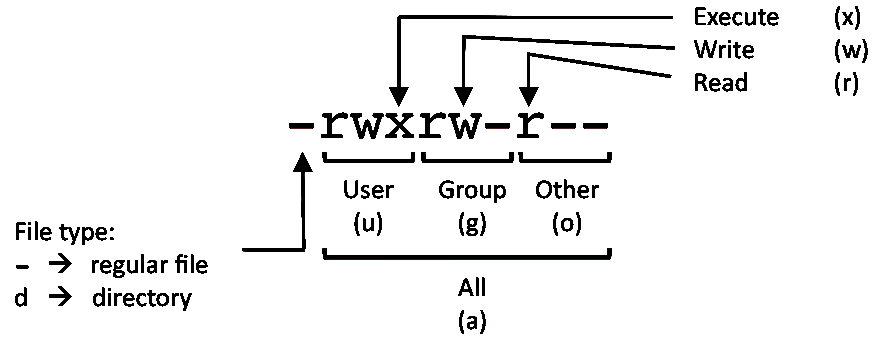
The file permissions listed above tells us the following:. The command takes the general form:. Chmod -R 755 /var/www/html There are two ways available to change file permissions on Linux.
Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions. It’s also possible to add permissions incrementally.
Set the permission of file.txt to "read and write by everyone.". $ chmod -R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command. It takes the following syntax:.
You can use -R to change permissions recursively. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:.
Using octal value & position:. In the previous example, the output showed that test.txt is a regular file with read and write permission assigned to the owner, but gives read-only access to the group and others. For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r--execute:.
The owner has read and write privileges. Chmod has two operating modes:. These can be used to keep someone from accessing the file, or say allow only a user to access or write a file to directory.
The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo. Add a sticky bit to a given directory:.
This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level of access to a file/folder for the users who access them. Accomplishes the same thing as the above command, using symbolic notation. In this example, you are setting permission to 0755:.
Using the “=” operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified. To have combination of permissions, add required numbers. The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value.
We can set permission for multiple files at once by using the chmod command. Changing File Permissions - Chmod The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory. 4 = r-5 = r-x;.
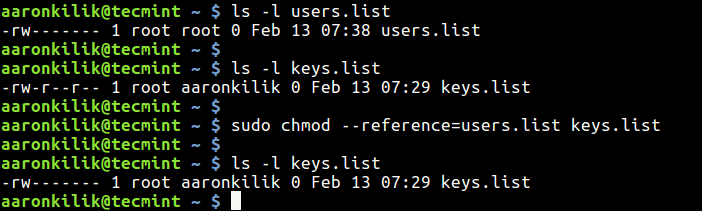
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. For instance, the Example directory contains three files (test1.txt, test2.txt, and test3.txt) with the same permissions (-rw-rw-r–). Now we want to remove the read and write permissions from the all users group.
In this example, file2’s permission will be set exactly same as file1’s permission. Chmod (this Tutorial's subject) and chown are designed to be able to change the defaults of user access as part of a secure plan by the Administrator, as well as, in the case of chown, modifying downloaded files to make them executable. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. Again as Rob has said, in 13,. You can use either the octal representation or symbolic representation to change the permission of a file or directory.
For example, if we want to set read and write permission for all text files, specify the *. Set the permissions of file.cgi to "read, write, and execute by owner" and "read and execute by the group and everyone else". X Permission to execute the file, or, in the case of a directory, search it.
$ chmod u+s file While to apply the sticky bit:. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax. Change File and Directory Permissions Using Chmod Command.
You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc. $ chmod --reference=file1 file2. You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux.
Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. The mode can also be specified using the symbolic method:. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of. Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which.

How To Change File Permissions Hostwinds Guides

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
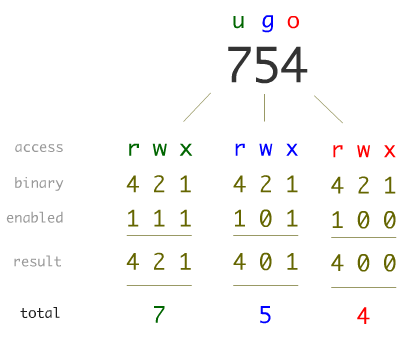
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
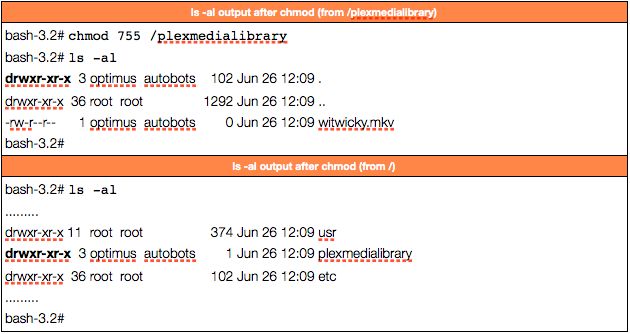
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
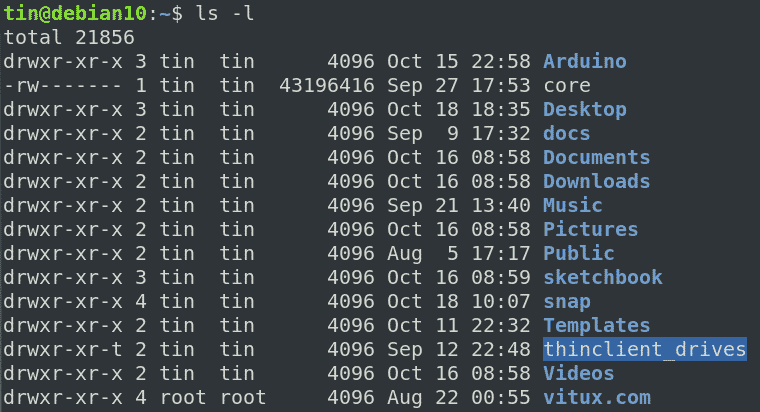
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
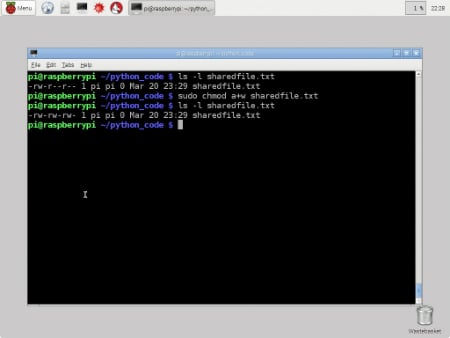
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
Linux Chmod Tips

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com
Linux File Folder Permissions
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions
Linux Command Cheat Sheet

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Ownership And Permissions
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Deciphering Linux File System Permissions Pressidium Managed Wordpress Hosting

Linux File Permissions For Beginners

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

File Security

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

What Are User And Group Permissions 荷树栋 开发者的网上家园
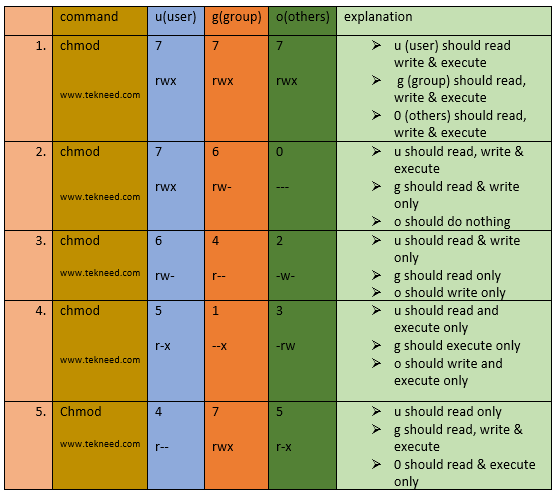
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders
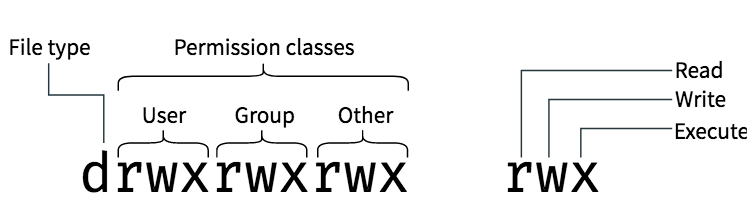
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
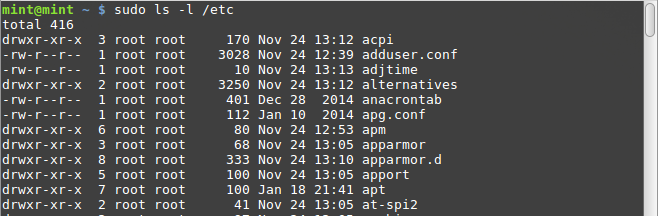
Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Understanding File Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How Do Linux File Permissions Work
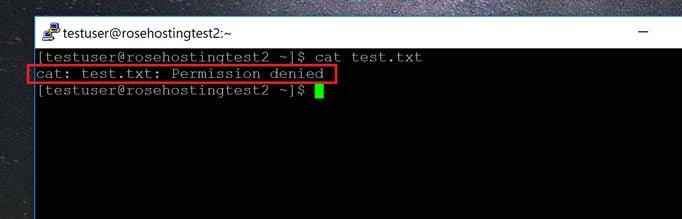
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought
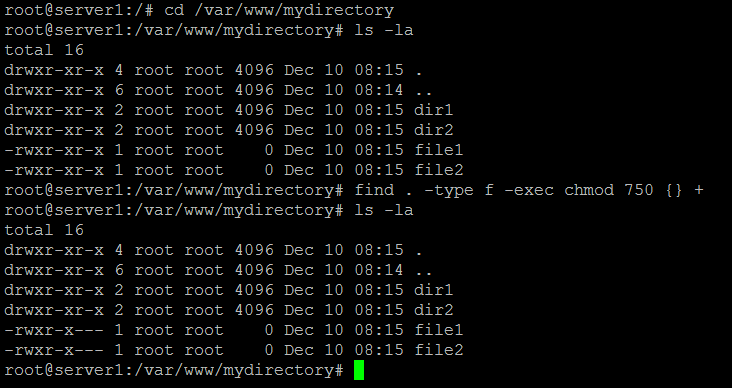
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
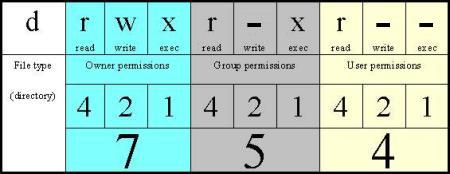
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
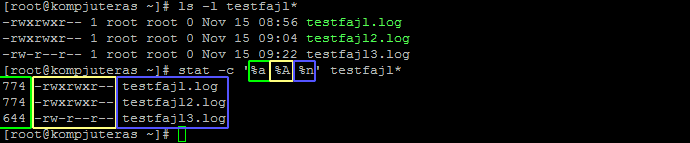
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras



